Causes and reasons for marine wastes
Now, let's reconfirm the problem we want to solve. It is to protect sea creaturesIn other words, reducing plastic that "flows into the sea". Now, let's reconfirm the problem we want to solve. It is to protect sea creatures. In other words, reducing plastic that "flows into the sea." Are all the plastics produced flown into the sea? How do they affect creatures and the environment?
Process of plastic going out to the sea
Is it true that plastics are flown into the sea? why? What is the path of plastics flowing into the sea?
①From land to sea
②Directly to the sea
Let's divide into these two routes and take a closer look.
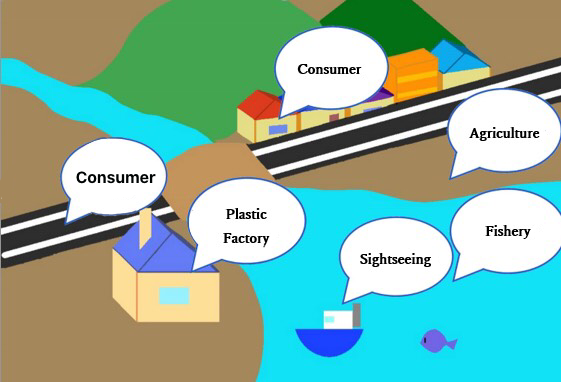
≪①From land to sea≫
⑴Plastic manufacturing and processing plant
During the production and processing of plastics, plastics may flow out of drains and into the sea. The types of plastics that are manufactured vary from factory to factory, but typical examples are pellets, beads, and fiber waste. As a countermeasure, manuals for handling plastics are being prepared, and it is important that employees be fully informed of them.
 Figure 1.Quoted from Plastic pellets from Japan Containers and Packaging Recycling
Figure 1.Quoted from Plastic pellets from Japan Containers and Packaging Recycling
⑵Consumers
From consumers, plastics such as plastic in containers and packaging, a synthetic rubber used in tires, shoes, etc. Flow from the land of homes and roads due to wind and rain. Also, clothing synthetic fibers and keratin removing granules in facial cleaners and toothpaste, which are small plastics used as so-called scrubbing material can be included in household wastewater and run out slipping through the sewage treatment.
Plastics for personal care products such as facial cleansers and toothpastes are increasingly replacing natural water-soluble materials. However, it is not completely obsolete.
⑶Agriculture
Examples include vinyl used in greenhouses and film fertilizers. Film fertilizer is a technology that covers the fertilizer with plastic and controls the fertilizer to come out of the shell when it is most effective according to the wishes of the farmer. The outflow of this shell into the sea is a serious problem, but on the other hand, it is difficult to use it as a substitute, partly because it reduces wasteful fertilizers and reduces the burden on aging farmers. It is considered to improve the performance of shell decomposition.
≪②Directly to the sea≫
⑷Tourism
During the ship's navigation, plastic flows into the sea just like domestic drainage. It is difficult to completely prevent spillage of fines such as fibers, even on ships that are very careful with garbage disposal and water purification. Also, plastic may be dumped directly onto the sea.
⑸Fishing
In the fishing industry, broken fishing nets, damaged fishing gear, and equipment used for aquaculture are left in the sea and still wander around the sea. The fact that fishing gear left in the water is harmful to aquatic organisms is called "ghost fishing". Fishing gear becomes finer due to deterioration and breakage. Recovery is very difficult.
There are two types of plastics in the sea; macroplastics of visible size, and microplastics of less than 5 mm in diameter.
Furthermore, microplastics are can be divided into 2 types; primary microplastics manufactured in a small size to use as raw materials to products (facial cleansers, cosmetics, industrial abrasives, etc.) and secondary microplastics which visible sized products were degraded by ultraviolet light or waves and subdivided.
Considering how plastic actually flows into the ocean, it is likely that plastic flowing into the ocean may not have been properly disposed of or disposed of in an inappropriate place, such as littering. The map shows the percentage of unmanaged plastic in the waste.
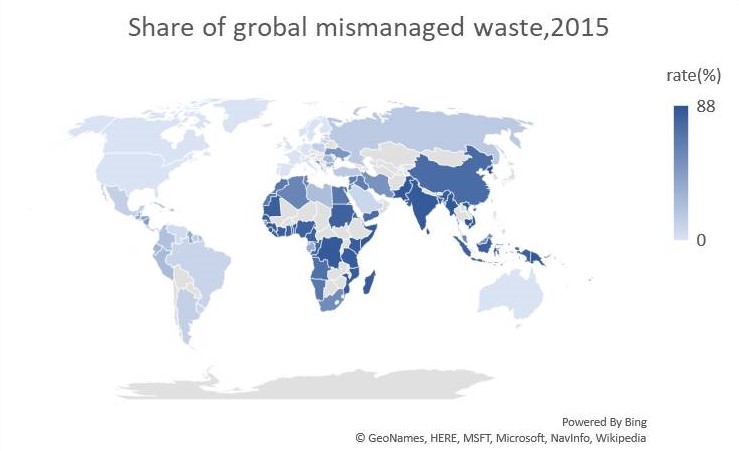 Figure 2.Jambeck, JR, Geyer, R., Wilcox, C., Siegler, TR, Perryman, M., Andrady, A., ... & Law, KL (2015). Input of plastic waste from land to ocean. Science, 347 (6223), 768-771.Create more
Figure 2.Jambeck, JR, Geyer, R., Wilcox, C., Siegler, TR, Perryman, M., Andrady, A., ... & Law, KL (2015). Input of plastic waste from land to ocean. Science, 347 (6223), 768-771.Create more
* "Not managed" means that has not been done appropriate waste disposal, such as littering or factory spills.
So far we've explored how plastic garbage flows into the sea. Now let's take a look at what happens when plastics are spilled into the sea.
