Home>Fermentation that save the world>5.Bioplastic
Section5. Bioplastic
Plastics are light and can be molded freely and are durable and convenient. However, they have the property that they do not decay (are not decomposed by microorganisms), so they exist forever.
Wood is broken down by microorganisms, but plastics are not broken down when buried in soil, and when burned emits harmful gases and carbon dioxide.
A large amount of plastic waste we disposable, such as plastic bottles, plastic bags, plastic containers and other synthetic resins, and synthetic fibers from clothes, flows into the sea, damaging marine life and adversely affecting ecosystems and the global environment.
You. In addition, petroleum as a raw material is a limited resource.
Bioplastics" were developed against this background.
It is made from various types of plastic raw materials made by fermenting microorganisms using starch and sugars derived from plants such as corn and potatoes.
A typical example is bioplastic using “Polylactic acid”.
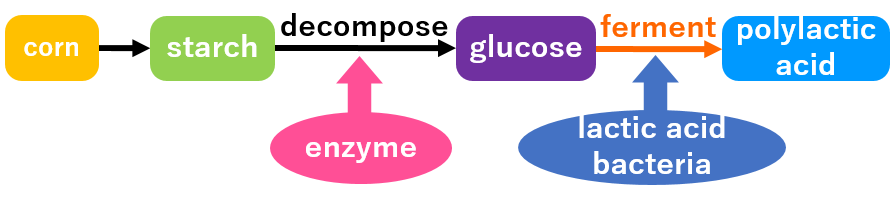
Polylactic acid (PLA) is made of starch, such as corn for livestock feed, from the same polyester as polyethylene terephthalate (PET), a material used for PET bottles.
This starch is broken down into glucose with enzymes, fermented with lactic acid bacteria to make lactic acid, and a lot of it is connected to polylactic acid.
Polylactic acid can be used in a variety of applications, such as garbage bags and agricultural materials as well as cell phones and personal computer housings.
In a familiar example, it is used for the window part of a window envelope.
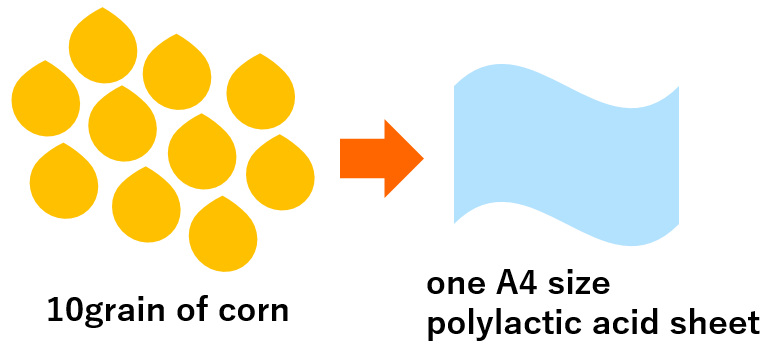
We can make one A4 size polylactic acid sheet from 10grain of corn.
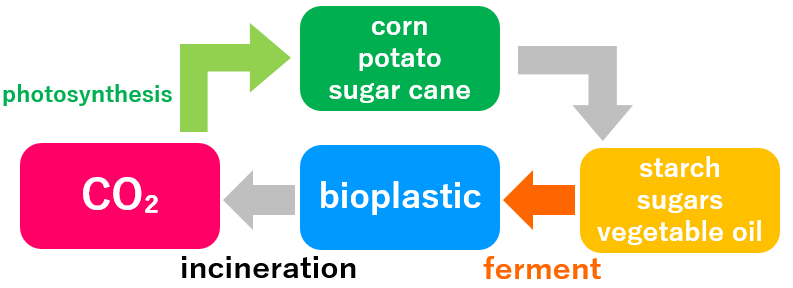
It is said that bioplastics are decomposed by the action of microorganisms and eventually become carbon dioxide and water.
When incinerated, it emits carbon dioxide, but since the original raw material of bioplastic is a plant, it is formed by absorbing carbon dioxide during growth. So, in theory, it is considered a carbon-neutral material that does not increase carbon dioxide and produce a greenhouse effect.
It is also called “Green plastic” because it is eco-friendly and environmentally friendly.
However, in order to produce bioplastic raw materials by fermentation, nutrients and energy are needed to make microorganisms work in an appropriate environment.
Unusable parts must be discarded. These are also thought to cause an increase in carbon dioxide and environmental load.
Technology development is progressing all over the world, but there are many challenges, and there are many things that do not know which technologies can reduce carbon dioxide, how much, and when.
What can we do now even this circumstance?
What actions do you take to reduce plastic waste?
Is it important to use plastic products carefully, consider other uses before disposing of them, and recycle and conserve resources?
Fermentation is expected to make bioplastics more efficient and contribute to environmental issues, but it is also important to take action now, considering what we can do.