Immunity dictionry
>More about immunity>Immunity dictionry
Immunity dictionary
Cells fighting on the front line

These cells patrol the body to find and eliminate antigens.
Neutrophils primarily eliminate the antigen itself.
Natural killer cells mainly eliminate infected cells.
Eosinophils mainly eliminate parasites around the mucous membrane, which is easily in contact with the outside of the body.
Although there are many unclear points about basophils, it is said that they release histamine and cause allergic reactions.
Cells that collect information while fighting
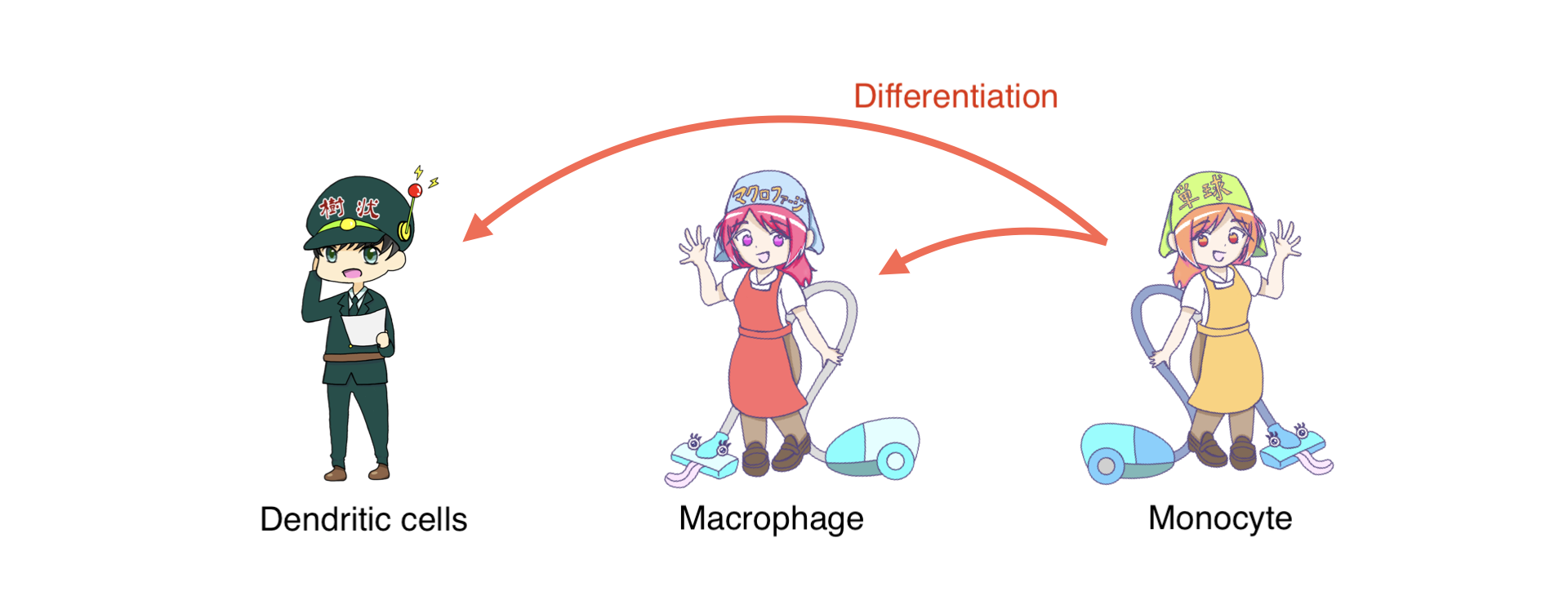
These cells have the role of feeding the antigen and passing fragments of the antigen to helper T cells .
Both dendritic cells and macrophages are differentiated from monocytes.
Macrophages also have the role of cleaning dead red blood cells and platelets.
Organized immune world elites
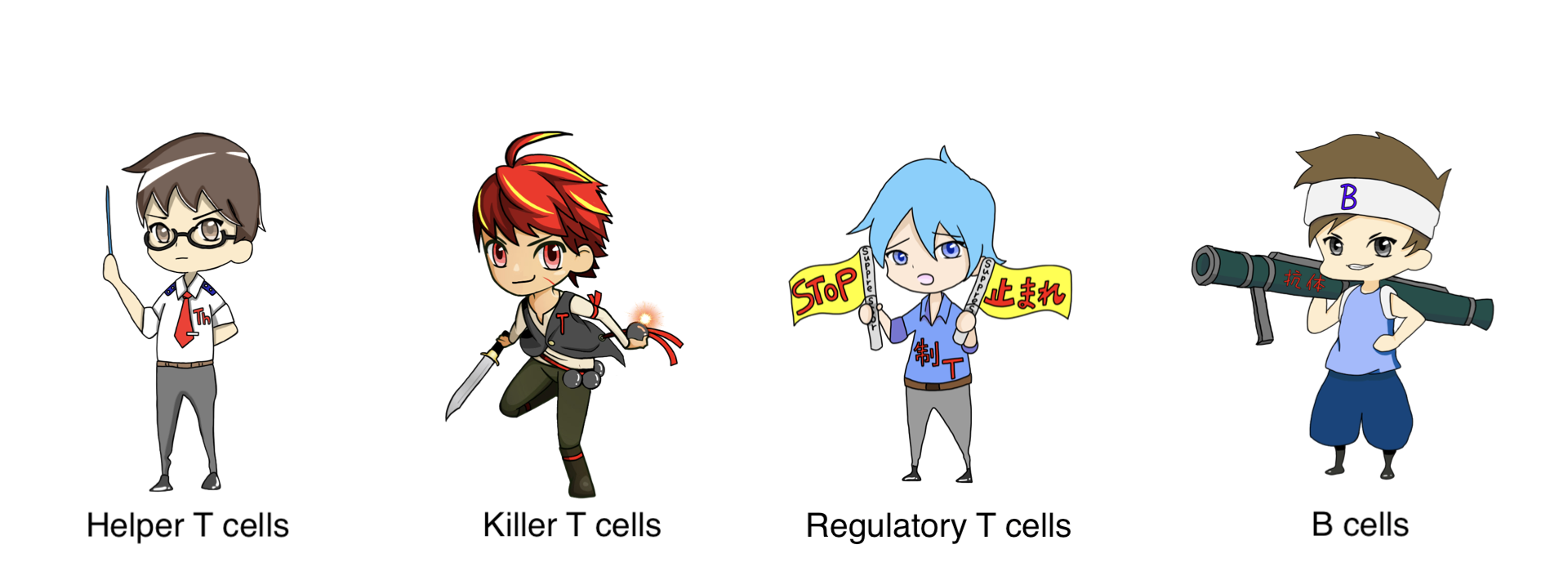
Killer T cells and B cells are activated by receiving commands from helper T cells.
Killer T cells destroy infected cells along with the pathogen.
The difference from natural killer cells is that killer T cells do not work unless ordered.
B cells make and release antibodies, which are substances that suppress the activity of antigens.
Regulatory T cells prevent helper T cells from give commands and prevent excessive immune activity.
| Immune cells | Overview | |
|---|---|---|
| Granulocytes | Among white blood cells, cells that contain a large amount of granules inside the cell. When dyed with Giemsa stain, the ease of dyeing differs depending on the type of dye (acidic, neutral, basic), and it is classified as follows. | |
| Neutrophils | A representative of innate immunity, which accounts for 50 to 70 % of white blood cells. It devours, digests and sterilizes foreign substances that have invaded the body. Lifespan is less than one day. | |
| Eosinophils | It exists in tissues that are easily exposed to the external environment, such as the respiratory, intestinal tract, urinary epithelium, and genital epithelium. It treats pathogens such as parasite larvae. It is involved in allergic reactions together with basophils and mast cells. | |
| Basophil | It acts like mast cells that are in tissues.It is activated by antigens and the like, releases histamine and the like, causing allergic symptoms. | |
| Monocyte | It is the largest of the white blood cells.It can be differentiate into macrophages and dendritic cells. When it moves into the tissue, it becomes a macrophage. | |
| Dendritic cells | It is differentiated from monocytes. It phagocytosis bacteria (phagocytosis) and passes some of them to T cells(antigen presentation). | |
| Macrophage | It is differentiated from macrophage monocytes. It phagocytosis bacteria(phagocytosis) and passes some of them to T cells(antigen presentation). It is a sweeper who preys on and digests not only antigens but also dead bodies such as red blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets. | |
| Lymphocytes | ||
| T cells | It is born in hematopoietic cells, differentiates and matures in the thymus. It is classified into multiple categories by their roles. | |
| Helper T cells… It receives information on the antigen presented by dendritic cells and activates B cells and macrophages. |
||
| Killer T cells(Cytotoxic T cells) … It receives information on the antigen presented by dendritic cells and attacks and eliminates harmful cells. |
||
| Regulatory T cells… It suppresses B cells from producing antibodies and stops the immune response. |
||
| B cells | It is differentiated and matured in the bone marrow or spleen. It synthesizes and releases antibodies (immunoglobulin) that bind to bacteria and viruses and neutralize them. | |
| Memory B cells… Among B cells, it memorizes information on pathogens that they once met. It lives for decades. |
||
| NK cells | It has a high killing ability. It attacks and eliminates cells infected with viruses and cancer cells. It is a type of innate immunity. |
Other cells that is related to immunity

It releases histamine in response to specific antibodies, causing an allergic reaction.
| Cells | Overview |
|---|---|
| Mast cells | It is one of the cells differentiated from hematopoietic stem cells. It exists mainly on the skin and mucous membranes of tissues that come into contact with the outside world. It secretes immunoglobulin IgE and causes an allergic reaction. During an allergic reaction, it releases chemical messengers such as histamines that are in cells. Histamine acts to constrict bronchial smooth muscle, increase vascular permeability, and secrete mucus. It also causes allergic symptoms. |
| Hematopoietic stem cells | It is the cells that are the source of blood cells such as red blood cells, white blood cells, and lymphocytes. It exists in the bone marrow and divides without differentiation and maturation. |
Terms
| Terms | Overview |
|---|---|
| Granules | It is a granular structure found inside a cell. There are various types and each has its own role. |
| Giemsa stain | It is one of the staining methods to color specific cells and tissues. It is used to visualize bacteria and cells in the blood. |
| Phagocytosis | It is the action that phagocytes take in substances and decompose and absorb them. |
| Histamine | It is a substance that has actions such as making it easier for blood to leak from blood vessels (improving vascular permeability) and vasodilation. If it is over-secreted, it can trigger allergic reactions and inflammation. |
| Antigen presentation | After macrophages and dendritic cells prey on foreign substances that have invaded the body, some of the invaders appear on the cell surface. That information is then passed to the T cells. This is "antigen presentation". |
| Differentiation/Maturity | It is the transformation of cells into more specialized and complex cells. |
| Thymus | It is the organ that destroys and matures T cells born from hematopoietic stem cells. |
| Pancreas | An organ that destroys old red blood cells and matures B cells and T cells. It is located on the left, upper abdomen of the body. |
Summary


