The Definition of Hot Springs
Chart
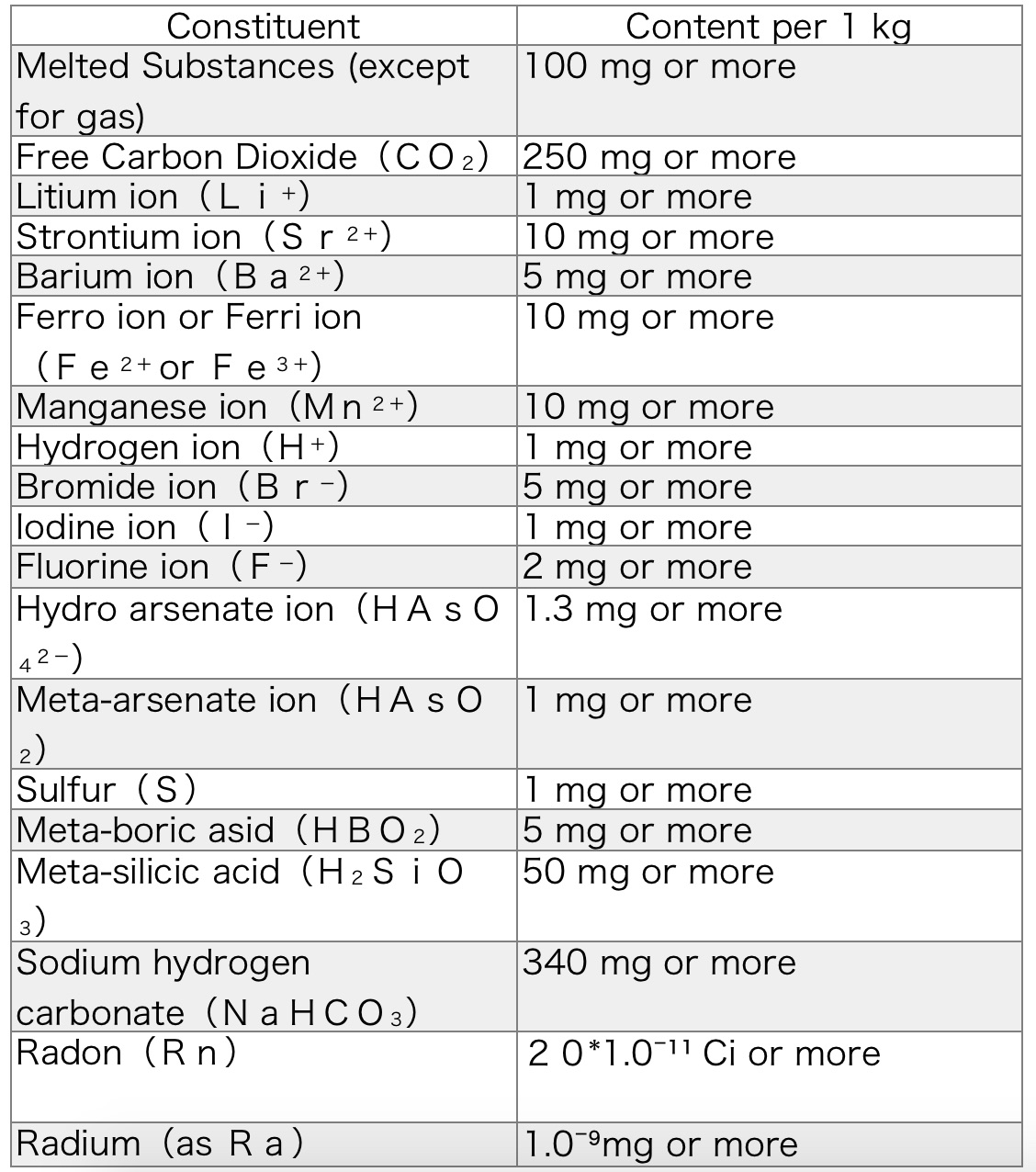
The definition of hot springs is established by Hot Springs Act. In a warm water spouted from underground, hot springs means an object including specific component more than constant quantity.
Hot Springs Act. Article 2
In this law, 「Onsen(hot spring)」means an object including substance or degree with the appendices in a warm water spouted from underground and mineral water, vapor and the rest gas(except natural gas of which main ingredient) is hydrocarbon.
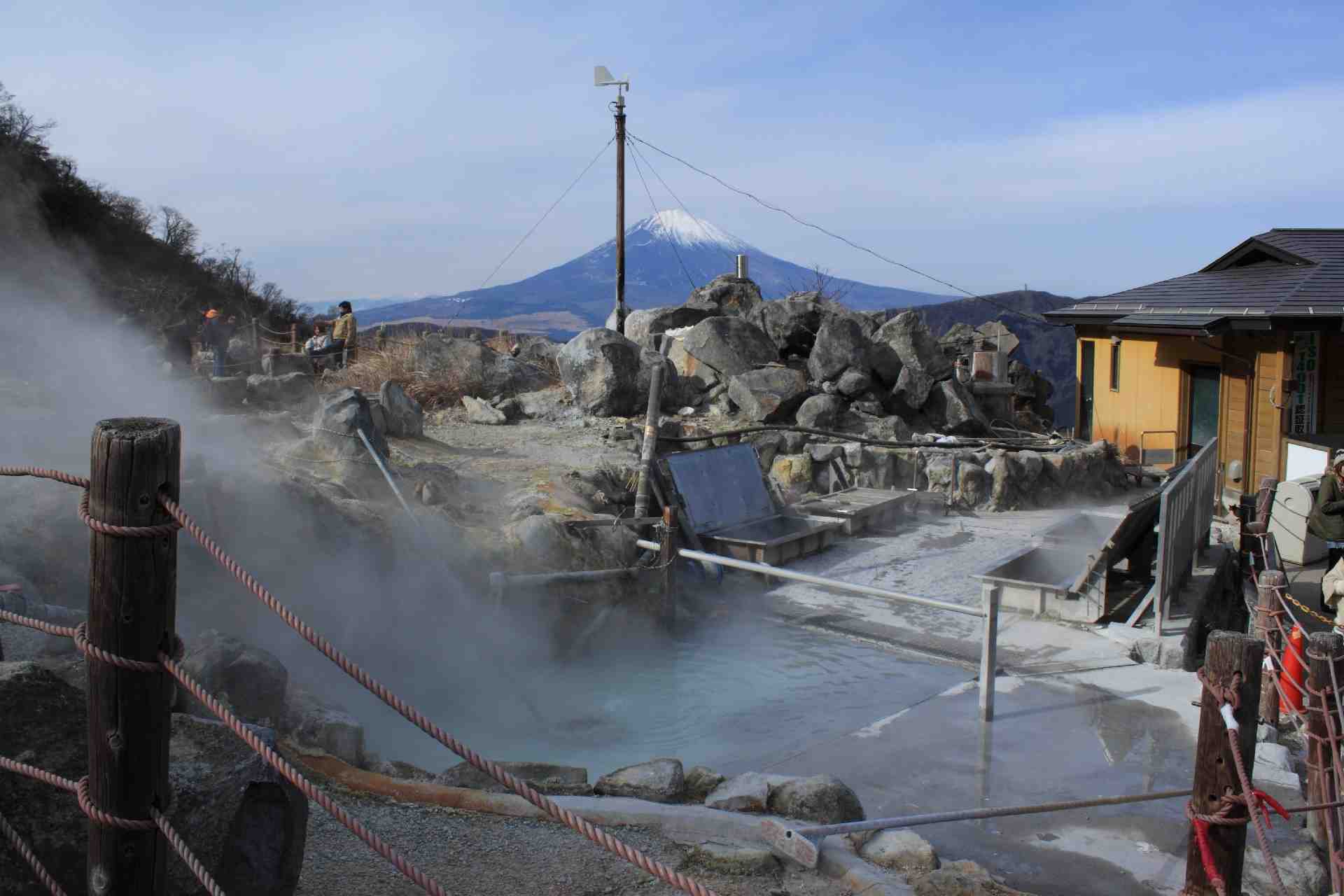
Hot Spring Situation in Japan

Hot Springs
According to the survey in 1970’s, there were hot springs more than 2,200. Then number of hot spring has been increasing more and more. And according to Ministry of the Environment, the number of hot springs which have place of stay is about 3,000, hot spring source is about 23,300 and hot spring facility is about 21,000 reaches. There are each 100~300 hot springs in Germany, Italy, Spanish and French and there are about 1,500 in all Europe. So it is obvious in Japan that number of hot springs is a large.
Volcanic Hot Springs and Non-volcanic Hot Springs
Hot springs have two type, volcanic hot spring and non-hot spring. These are divided into by difference of heat source. Let’s see detailed about them.
Volcanic Hot Springs
Volcanic hot spring is hot spring that magma is a heat source. Volcanic hot spring originated in high temperature water which is such as rain added gas composition emitted from magma, in addition, it is dissolved various components from around rock and stratum. Magma is too high temperature, so water is also too high temperature. High temperature water whose degree is more than 370 degree is supercritical state.
Supercritical state means it has both water(liquid) and water vapor(gas). Much many components can be dissolved in high temperature water by this state. However, when the temperature close to the face of the earth, high temperature water cannot be supercritical state, it is divided into gas and liquid. Water is dissolved in such as water-soluble salt , sodium hydrogen carbonate and metal ion, gas is dissolved in hydrogen sulfide, carbon dioxide and hydrogen chloride. The gas can dissolve in groundwater, so it makes strong acidity hot spring. On the contrary, water which have many water-soluble components become slightly alkaline common salt springs. Simply put, as leaving from fumarolic field, spring quality distribution acidic springs~acidic sulfur springs, strong acidic sulfur saline spring, acidic sulfate spring, weak acidic~neutral sulfur saline, alkaline hydrogen carbonate saline. For example, in Beppu hot spring by Ooita Prefecture, various spring quality’s is seen from fumarolic field to the coast.
Based on the factors, volcanic hot spring is including salt but you know this salt was not carried never from sea water. Water divided from magma include many salt at first.
Non-volcanic Hot Springs
Non-volcanic means hot spring heated by ground temperature.
Most of these that erstwhile seawater and ground water were shut in stratum and it were heated by ground temperature. Besides, in case of many organic matter including in stratum, it is sometimes 「Kuroyu(black hot water)」. This type of hot sprig are seen common around Tokyo Bay.

