|
Description
|
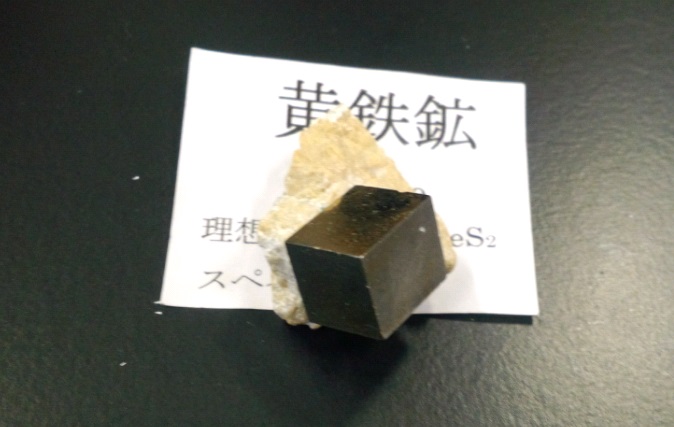
Iron pyrite is hte most common of the sulfide minerals. Pyrite is usually found associated with other sulfides or oxides in quartzveins, sedimentary rock, and metamorphic rock, as well as in coal beds and as a replacement mineral in fossils. Iron pyrite is mostly cubic. The faces may be striated, but it is also frequently octahedral and pyritohedron.
This mineral's metallic luster and pale brass-yellow hue give it a superficial resemblance to gold, hence the well-known nickname of fool's gold. Iron pyrite is distinguishable from native gold by its hardness, brittleness and crystal form. Natural gold tends to be anhedral , whereas pyrite comes as either cubes or multifaceted crystals. The name pyrite derivies from the Greek word ügâ╬üh meaning in fire. In ancient Roman times, this name was applied to several types of stone that would create sparks when struck against steel.
|



 Pyrite
Pyrite



