Immunity × History
>More about immunity>Immunity × History
The presence of immunity that people have begun to notice
Hundreds of years ago, in response to the plague epidemic, Christian knights and monks performed charity activities such as treating patients. Some of the knights were infected with the plague, but miraculously recovered.They did not become infected with plague even if they came into contact with infected patients. At that time, people believed that the phenomenon was due to God’s help, and the Pope exempted those who recovered from the plague from work and tax allocations (im-munitas). This occurrence is the origin of the word immunity.
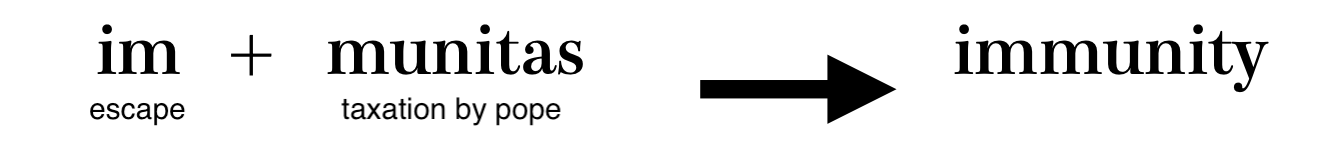
Previous vaccine –curse-like prevention of smallpox –
Over 2000 years ago, there was an epidemic of smallpox. At that time, it was well known in West Asia, India and China that smallpox had strong immunity. Using this idea to apply small amounts of extract from smallpox patient to healthy people, they became less likely to become seriously infected with smallpox thereafter.
However, at that time there was no concept of "immunity", so it was treated as a curse-like method. In addition, such acts were synonymous with infecting people with smallpox, which exacerbated the condition of many and resulted in death.
Invention of modern vaccine
Since the mid-18th century, people became infected with the cowpox disease, "cowpox," sufferers had the advantage of not being infected with smallpox. This is because the smallpox virus and cowpox virus are similar in nature and structure, so if you acquire immunity to the cowpox virus, you can also acquire immunity to smallpox. Focusing on this phenomenon, Edward Jenner developed a smallpox vaccine by cowpox inoculation in 1798. In addition, cowpox has very mild symptoms compared to smallpox, so it is highly safe.
Edward Jenner later became known as the "father of modern immunology."
Clarification of vaccine mechanism
Though Jenner invented the first vaccine, it was an empirical invention and the biological mechanism was not well understood. It was the French biochemist Louis Pasteur who finally explained the scientific mechanism behind the vaccine function.
The beginning of serology
Shibasaburo Kitazato, along with Dr. Behring, said that the immunity gained by vaccination is "an antibody in the blood".
This discovery led to the development of methods for removing antibodies from animal blood and using them to treat human diseases.
It was called "serum therapy" because it is a treatment method in which serum (an extract of antibody components in the blood) is injected into the human body.
However, Russian microbiologist Ilya Ilyich Mechnikov thought that "the function of cells in the blood and the function of biological defense" is the true nature of immunity.
To the present age
Many discoveries in immunology have been made with the rapid development of science.
Recently, Dr. Tasuku Honjo has developed Opdivo, a drug that promotes an immune attack on cancer cells.
Even now, new discoveries are being made, and there are still many unsolved mysteries in the field of immunity.
Summary


