1.This is a worrisome problem.
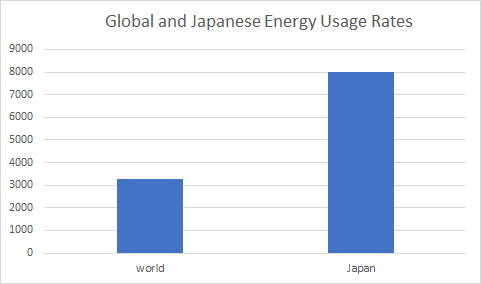
The average per capita consumption of electricity in the world today is
3260 kwh, but Japan's consumption is higher than that at 8010 kwh. This
means that more electricity is required in Japan than in other countries.
However, there is a worrisome problem.
source; https://www.kepco.co.jp/sp/energy_supply/energy/nowenergy/japan_energy.html
|
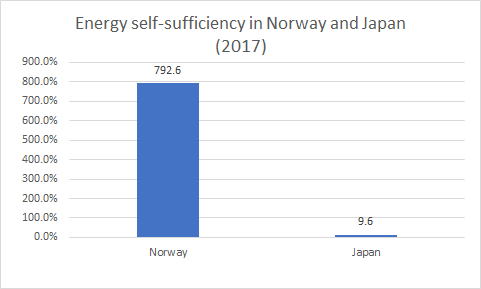
2. Japan's Energy Self-Sufficiency Rate
Japan is a member of the OECD, the Organization for Economic Cooperation
and Development(OECD) which is an international organization whose members
are mainly from developed countries in Europe. Among the 35 countries in
the OECD, Norway has the highest energy self-sufficiency rate at 792.6%,
while Japan's energy self-sufficiency rate is only 9.6%.(100% means that
a country can provide its own electricity in its own country.)
sourse:https://www.enecho.meti.go.jp/about/special/johoteikyo/slideshow_01.html |
sourse:https://www.kepco.co.jp/sp/energy_supply/energy/nowenergy/japan_energy.html |
sourse: https://www.enecho.meti.go.jp/about/special/johoteikyo/slideshow_01.html |
3. Energy Imports
Japan imports oil and other resources from Iraq and Saudi Arabia due to the scarcity of domestic resources. The breakdown is as follows: Saudi Arabia 40%, United Arab Emirates 36%, Kuwait 13%, and Qatar dash 11%.
source:https://looop-denki.com/home/denkinavi/energy/powergeneration/energyissue/#:~:text= |
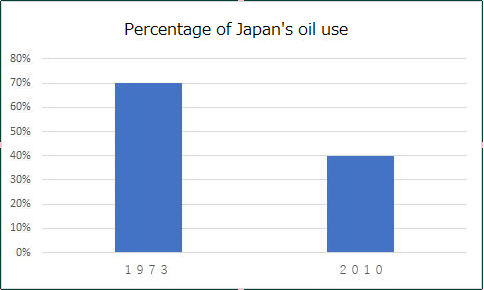
4. What energy has been relied on in the past compared to the present?
In 1973, oil was the main source of energy in Japan, but the oil crisis
brought oil usage down to 40% in 2010. Elsewhere, nuclear power dropped
from 10% in 2010 to 1% in 2017 after the Great East Japan Earthquake. The
reason why nuclear power has not been utilized as much is because the Great
East Japan Earthquake caused an accident at a nuclear power plant, and
nuclear power plants were shut down.
source;https://www.enecho.meti.go.jp/about/special/johoteikyo/slideshow_01.html |

source:https://looop-denki.com/home/denkinavi/energy/powergeneration/energyissue/#:~:text= |
source;https://www.enecho.meti.go.jp/about/special/johoteikyo/slideshow_01.html |
5.What Are Renewable Energies?
Renewable energies include solar power, wind power, geothermal power, small
and medium-sized hydropower, and biomass. They are characterized by the
fact that they do not emit greenhouse gases, can be produced domestically,
and contribute to energy security. In Japan, renewable energies account
for 10% of electricity generated, and solar power generation is the most
common type of renewable energy.
sourse;https://www.enecho.meti.go.jp/category/saving_and_new/saiene/renewable/outline/index.html |
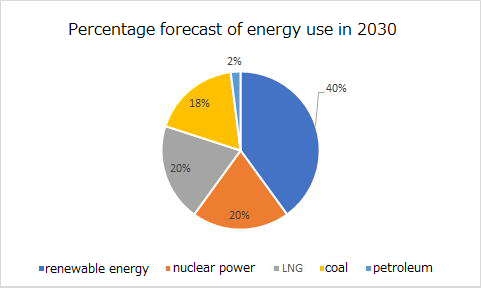
6. Energy of the Future
Renewable energy is one current source of energy . In Japan, renewable
energy is expected to account for 40% of all energy in 2030, with nuclear
power at 20%, LNG (liquefied natural gas) at 20%, coal at about 20%, and
oil at 2%.
source; https://www.jaero.or.jp/sogo/detail/cat-01-04.html |
  |
source; https://www.jaero.or.jp/sogo/detail/cat-01-04.html |
7. Electricity Consumption at Home
Although the number of people living in each household differs, the electricity
consumption of one person is roughly 6.1 kwh per day. 2 people living together
is about 1.7 times that of one person, 3 people living together is about
2 times, 4 people living together is about 2.2 times, and 5 people living
together is about 2.4 times that of one person.
source;https://www.yumesolar.jp/column/power-consume/ |
8. Household Appliances that Consume the Most Electricity
Refrigerators are the largest consumer of electricity in the household
at 14.2%, followed by lighting fixtures at 13.4%, other home appliances
at 8.9%, air conditioners at 7.4%, electric water heaters at 5.4%, eco-cutes
at 3.8%, and other appliances at 46.9%.
source;https://www.ecostylepower.com/denki_column19/ |
eigo.png)
source:https://www.yumesolar.jp/column/power-consume/ |

source;https://www.ecostylepower.com/denki_column19/ |












