Types of Light
<Electromagnetic waves (Emitted light)>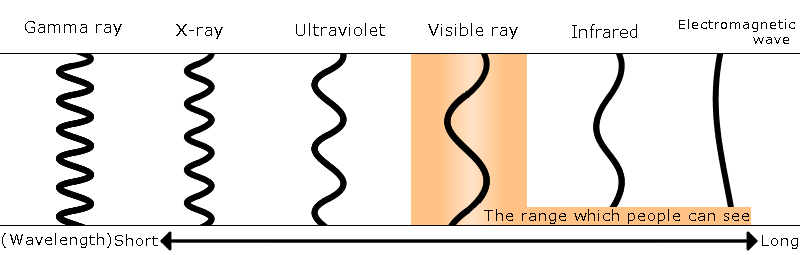
Electromagnetic waves are waves formed by periodic changes in electromagnetic fields. the direction of moving charged particles is bent by ※1the lorentz force of magnetic fields,and an electromagnetic wave is generated. Electromagnetic waves have a continuous spectrum with a wide range from microwaves to X rays. Artificial electromagnetic waves have a spectrum with a range from infrared rays to X rays,while natural electromagnetic waves range from electric waves to gamma rays,It is rare to limit and call especially visible light. Almost all electromagnetic waves called emitted light are artificial.
※As shown in the figure, light is classified according to wavelength, but it is not necessarily always clearly divided. Different electromagnetic waves sometimes have the same wavelength.
Electric wave (wavelength: 1mm-100km)
An electric wave differs in nature among different wavelengths. So,it used for various things such as optical fiber communications systems, microwave ovens, mobile phones, television, marine radios, etc.Infrared rays (wavelength: 750nm-1mm)※2
this spectrum's wavelengths an longer than the normal spectrum of red. Infrared ray's wavelengths are longer than visible light, and shorter than electric waves. Their penetration ability through the air is large. Since their thermal action is large, infrared rays are also called heat rays. Infrared rays are divided into near-infrared (0.7-2.5μm)※2, mid-infrared (2.5-4μm),and far-infrared (4-1000μm) by their wavelengths.・Near-infrared・・・This has properties similar to visible light.This is used for "infrared communication" and "infrared cameras".
・Mid-infrared・・・This is sometimes part of the near infrared.This is also called training light
・Far-infrared・・・This has a heating effect.This is clean and safe energy.
Visible light (wavelength :about 380nm - about 750nm)
this is light that can be seen by humans. Visible light is usually present in a mixture of different wavelengths,so it looks white. When you separate the light of fluorescent lamps into different wavelengths with a prism,you'll see the different colors in each wavelength. In Japan,the colors are ordered as purple, blue, green, yellowish green, yellow, orange,and red from shortest to longest wavelength and is called the rainbow. However,this classification differs between countries and cultures as does the color of a rainbow. (Go to detailed columns of the rainbow) The full range of color state changes according to wavelength is called the color spectrum.Ultraviolet rays (wavelength: 10nm-380nm)
This spectrum's wavelengths are shorter than violet. UV ray7s wavelength is shorter than visible light, and longer than X rays.It is in sunlight. Because the chemical action is clearly seen,they are also called actinic rays. UV rays are divided into near ultraviolet rays, far ultraviolet rays,and extreme ultraviolet rays by wavelength.○Near ultraviolet (wavelength: 200nm 〜 380nm)
This type is further divided into UVA (long wavelength ultraviolet rays), UVB (medium wave ultraviolet rays),and UVC (short wavelength ultraviolet rays).
・UVA (wavelength: 315nm 〜 380nm)
This acts on the dermis layer of the skin and it denatures proteins found there. It is related to a shift in the substance of skin cells their activation. Melanin produced by UVB exposure is oxidized and darkens skin. (Suntan)
・UVB (wavelength: 280nm 〜 315nm)
Although this energy also acts on the epidermal layer, pigment cells generates melanin as a defensive reaction. This is called tanning. (Sunburn)
・UVC (wavelength: 200nm 〜 280nm)
Since these rays are blocked by the ozone layer, they cannot reach the surface. Since it has a strong sterilizing power, it's destructiveness to a living things is the highest. The ozone layer is being damaged by global warming and the effects of this on organisms on the ground are concerning.
While the atmosphere of the earth, some ultraviolet rays are blocked by ozone layer and UVC is blocked almost completely. However,the problems caused by depletion of the ozone layer are increasing,as more ultraviolet rays are able to penetrute and do more damage, contributing to further layer depletion and periodic ozone holes.
○Far-ultraviolet radiation(wavelength: 10〜200nm)
Since it can not exist outside of a vacuum, it is also called vacuum ultraviolet rays(VUV). Since it is absorbed by the atmosphere, it does not make it to the surface of the Earth.
○Extreme ultraviolet (wavelength: under 10nm)
Just like far-ultraviolet, it is absorbed by the atmosphere and does not make it to the surface. The strength of this energy changes significantly solar activity every 11 years.
X rays (wavelength : 0.01-10nm) and Gamma rays (wavelength: under 10pm)※2
These have shorter wavelengths than ultraviolet waves,and very high energy.They are generally referred to as radiation. X-rays can be produced artificially,but because gamma rays are emitted naturally from a nucleus,they can not be controlled artificially.[The effect of electromagnetic waves on living organisms]
Far-infrared 〜 mid-infrared are considered absorbable light as they are easily absorbed by organisms. So,it works to create heat in living bodies.
Near-infrared 〜 ultraviolet are considered reflected light as they are not absorbed into object(including animals and plants) on the Earth. So,they work only to divide the cells of plants and animals.
X rays 〜 Gamma rays are considered transmitted light as they are easily and deeply absorbed into the cells of plants and animals. This absorbed energy can damage DNA and can cause malformations and cancer.
<Other kinds of light>
Sunlight
Light emitted by the sun. (Visible light, infrared, ultraviolet and so on.) The time sunlight takes to reach the Earth is about 8m 17s〜19s. We usually feel only a small part of the sunlight because most of the light is absorbed by the atmosphere and ozone layer. It is used for such things as sundials and power generation.Laser beams
Laser beams emit light in a single wavelength ※3Thus it is possible to concentrate a high density of light energy. ※4 Lasers are classified into solid state, gas and liquid types depending on the substance used to ※3stimulate emission.◎【Video : Let's watch a laser】
・・・Laser beams hit floating chalk dust and you can see the passage of light as the light particles are scattered. This is called the Tyndall phenomenon.
※1 Lorentz force・・・the force which acts on moving charged particles in electromagnetic fields.
※2 1μm=10-6m , 1nm=10-9m , 1pm=10-12m
[1pm=0.001nm = 0.000001μm)]
※3 Stimulated emission・・・the phenomenon of emitting light when a substance, because of being interconnected with another substance or because of a certain interaction changes state from high energy to low energy. Then, the light emitted is proportional to external an electromagnetic waves.