Color of celestial bodies
The obiects we can see in the sky come in three types, planets, satellites, and distant stars.Planets and satellites
Planets and satellites reflect the light of other heavenly bodies, such as the sun, and shine.○Mars・・・Is covered with iron oxide, so it reflects red light.
○Jupiter・・・Is covered with methane, so it reflects yellow light.
○The heavenly bodies which reflect the most light(Venus etc.)・・・Reflects the original light directly.
○the Earth・・・Reflects blue light from the sea and the atmosphere.
Stars
A Star which emits its own light is called star. The wavelength of light energy and surface temperature affect the color of a star. When short wavelength blue light becomes stronger at higher surface temperatures, stars when become blue-white or purple. Conversely,when Longer wavelength red light becomes stronger as the surface temperature is lowered, stars become reddish. thus,when ignited in a gas ring , the portion of a star with a high temperature becomes blue and the portion with a low temperature follows the same principle to become red.The table below summarizes the colors of stars, surface temperature, a spectral type, and the typical stars applicable to these.
| Color | Surface temperature | spectral type | typical star |
|---|---|---|---|
| Red | 3000〜4000K | M-type | Antares, Betelgeuse |
| Orange | 4000〜5300K | K-type | Aldebaran, Arcturus |
| Yellow | 5300〜6000K | G-type | the sun |
| Cream | 6000〜7500K | F-type | Canopus, Procyon |
| White | 7500〜10000K | A-type | Sirius, Vega |
| Light blue | 10000〜30000K | B-type | Rigel, Spica |
| Blue | 30000〜50000K | O-type | Sigma Star Orion |
spectral type・・・A classification based on a stars emmission of light.
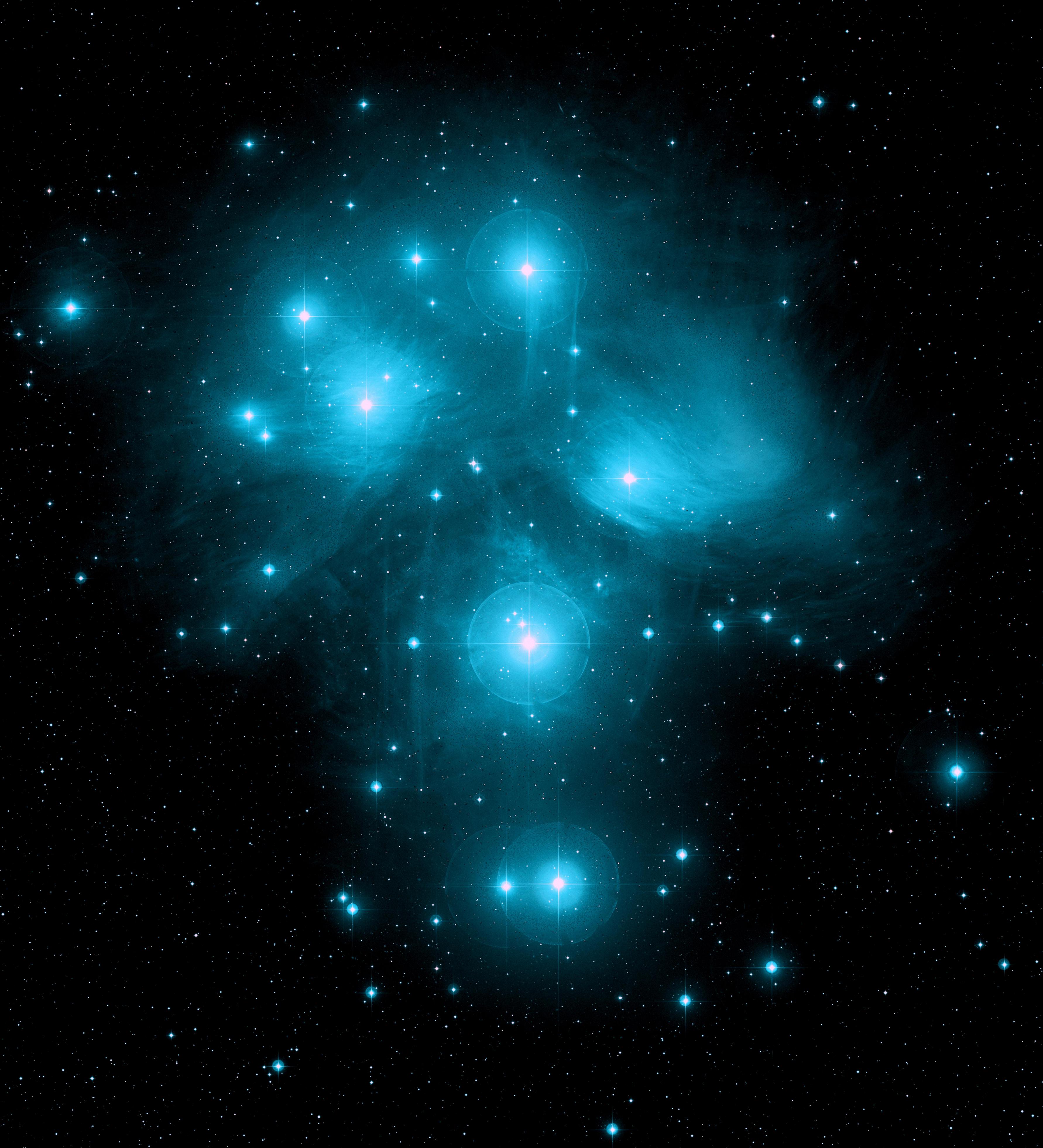

↑Blue stars
<Click to enlarge(Displayed in a separate window)>