Procedure for checking the criteria for determining unreasonable treatment differences ?
Check in the following order what the irrational difference is.
1.Check if you are hiring short-term or fixed-term workers
This is exactly what the name implies, so make sure you are hiring short-term or fixed-term workers. If so, segment them by employee type.
<Example: A supermarket example>
Classify by employee type as described above. It should be noted here that even the same part-time employee has different job contents between cashier and complaint processing, so they are written separately (Example 1 and Example 2 in the above example).| In-house part-time and fixed-time employees are classified by employee type | Short or full time | Fixed or non-fixed | Number or approximate number | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ex.1 | Part-time job (cashier) | Full | Fixed | 13 people |
| Ex.2 | Part-time job (claim processing) | Short | Fixed | 5 people |
| Ex.3 | Stocking | Full | Non-fixed | 23 people |
2.Check if there is a difference in compensation such as salary between short-time workers, fixed-term workers and regular employees
By the way, we divided employees in ①. Check if there are any differences in salaries, benefits, etc. between the classified employees and regular employees. Let's check according to the guidelines (guidelines) issued by the Ministry of Health, Labor and Welfare.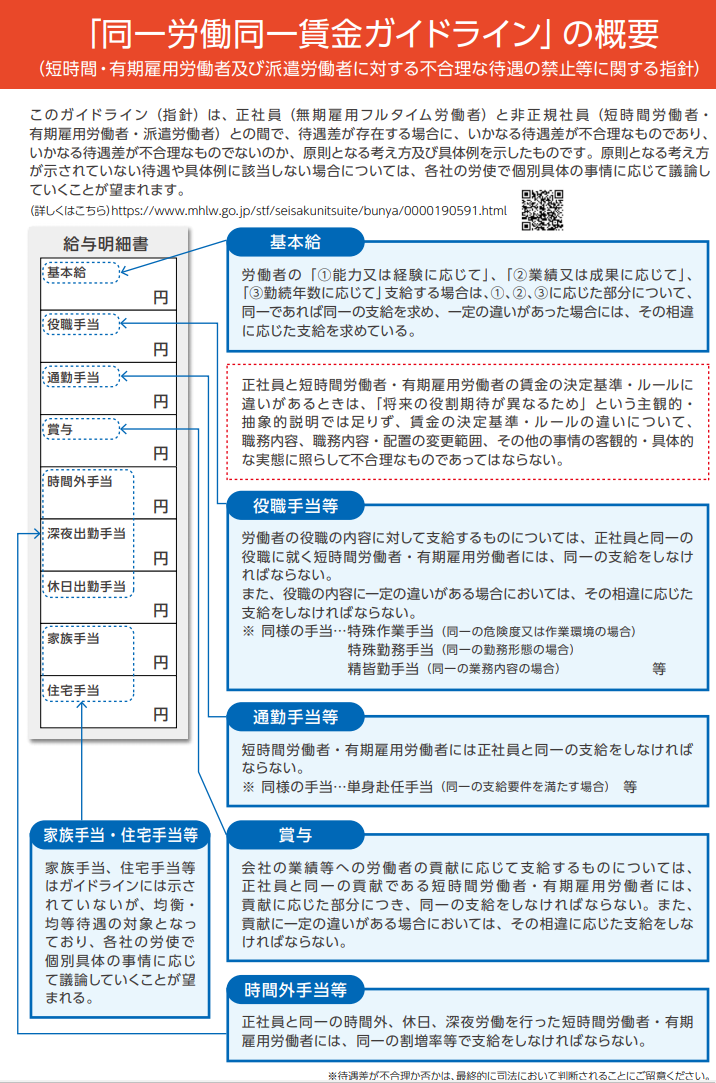
-Reference: Procedures for implementing part-time and fixed-term employment labor law-
3.Check the reason for the difference in treatment and the rationality of the reason
If so, find out why. You also need to make sure that the reason is not unreasonable.Find out what the difference is and why it isn't.
<Example>
| Why make a difference | Irrational or rational | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Example1 | Commuting allowance | Part-time workers are not paid to part-time workers because they have less work than regular employees. | Irrational |
| Example2 | Full-time allowance | We believe that the work of regular employees is heavy, and we pay only regular employees to encourage them to work more. | Irrational |
| Example3 | Bonus | Regular employees are paid bonuses because they have a quota, but part-time workers are paid a fixed amount regardless of their work because they have no quota and their contribution to the company is constant. | rational |
Commentary
Example1:The commuting allowance is an allowance to pay the expenses necessary for commuting, and it has little relation to the amount or content of work. So this is irrational.Example2:The belief that regular employees are responsible is subjective. This is not a good reason. So this is also irrational.
Example3:It is reasonable to point out the differences in the content of work between regular employees and part-time workers, and also to give part-time workers some bonuses.
In other words, to summarize the above points, an irrational difference in treatment means that confirmation or subjective judgment as to whether the allowance should be discriminated based on the job content is not good.
Explanation of three major changes in part-time labor law
Explanation about reform about childcare leave-

