Analysis of the human genome completed
There are other ethical issues besides designer babies: in 2000, the United States, Europe, and Japan announced that they had almost finished decoding the total human genetic information through international joint projects and private companies.
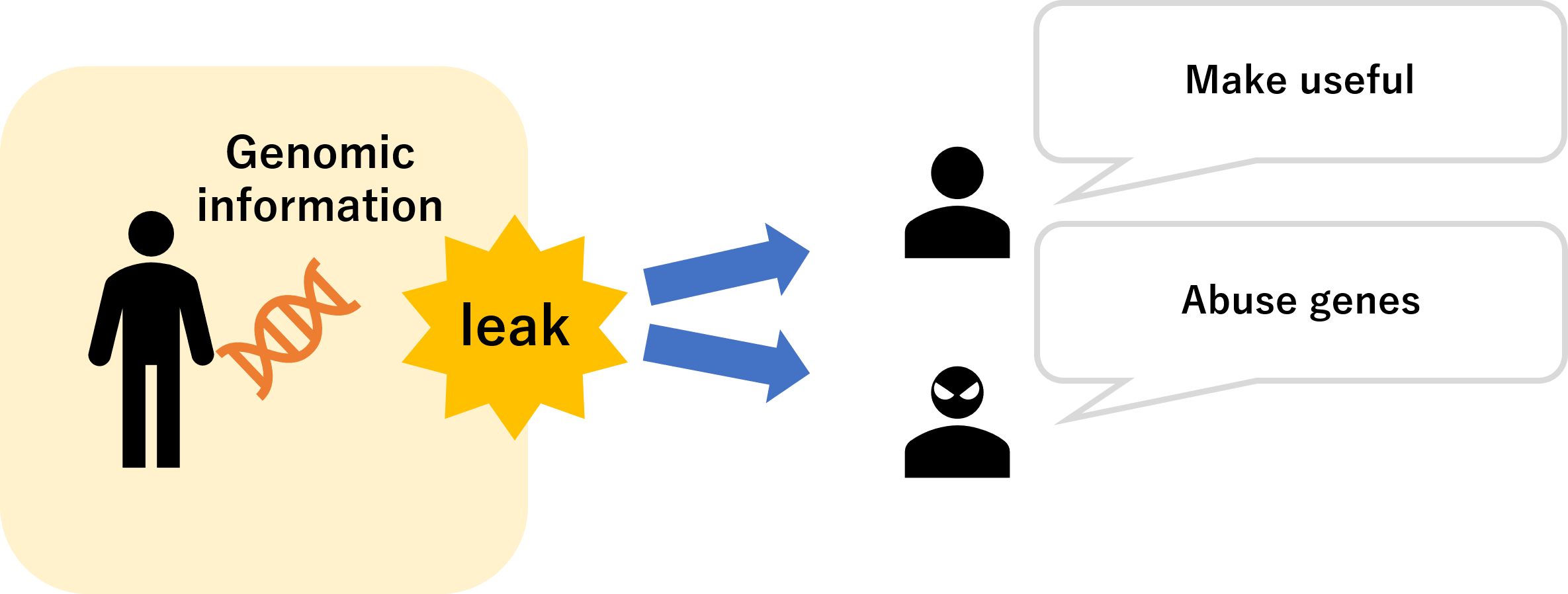
There is no doubt that the decoding of the human genome will lead to the development of bio-medicine such as gene therapy and genetic diagnosis, but it is not all good. The disadvantages are listed as follows
- Responsibility for the protection of personal information
- Measures against privacy leaks.
- The possibility of discrimination
There are many reasons for this. In order to solve these problems, strict penalties and regulations are required. The Bioethics Committee of the Council for Science and Technology Policy has formulated basic principles for human genome analysis.
The Committee on Bioethics of the Council for Science and Technology has compiled a set of basic principles regarding human genome analysis, which calls for obtaining informed consent and strict protection of personal genetic information.
In addition, the government has compiled "Guidelines for Addressing Ethical Issues Associated with Genetic Analysis Research".
Universal Declaration on the Human Genome and Human Rights
In the world, the United Nations adopted the Universal Declaration on the Human Genome and Human Rights in 1997. This declaration prohibits research on the human genome from impairing human dignity, human rights and freedoms, and prohibits discrimination.
The declaration prohibits research on the human genome from undermining human dignity, human rights and freedoms, and prohibits discrimination.
‟
-
(From the Preface) "Recognizing that research on the human genome and the application of its results offer vast prospects for progress in improving the health of individuals and humanity as a whole, but
Emphasizing, however, that such research should fully respect human dignity, freedom and human rights, and the prohibition of all forms of discrimination based on genetic characteristics
Adopting this Declaration. (With some changes.)
-
(From Article 5) "Research, treatment or diagnosis affecting the genome of an individual may be undertaken only after a rigorous prior assessment of the potential risks and benefits involved, and in accordance with other requirements of national law.
-
(From Article 6) "No one shall, on the basis of genetic characteristics, be subjected to discrimination with the intent or effect of violating human rights, fundamental freedoms and human dignity.
-
In the framework of research on the human genome, because of its ethical and social implications, the inherent responsibilities of the researcher's activities, including meticulousness, prudence, intellectual honesty, and integrity in the conduct of research and in the publication and use of research results, should be the subject of special attention.
It should be a subject of special attention. Public and private science policymakers also have a special responsibility in this regard.
It is believed that gene therapy will be more developed by human genome analysis, but there are still some problems in terms of privacy.
In the future, each individual will have genome information, and one's genome information may become one of the most important personal information.
In order to make effective use of genome information, we will need to develop technologies other than biotechnology.