


What Are Leeches?
Leeches is a general term for a group of annelid animals belonging to the class Hirudinoidea. Most species live in freshwater, but some species also live in saltwater and on moist land. Their bodies are adapted to a parasitic lifestyle, and they have suckers on both the front and back of their bodies. There are about 360 known species in the world, and about 60 species live in Japan. All species have 34 segments regardless of body size, but each segment is further divided into 2 to 14 segments, giving them the look of being divided into very many segments.
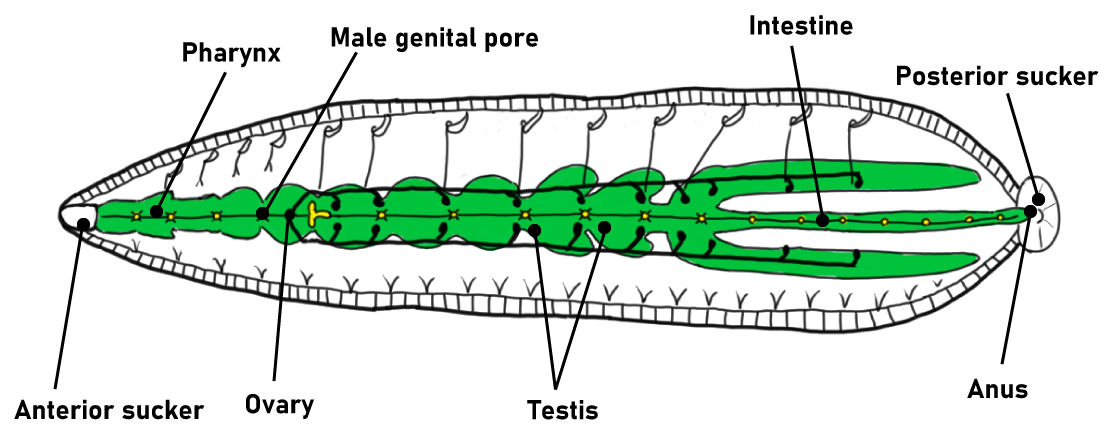
The Ecology of Leeches
They can be found when the temperature is above 25 degrees Celsius and it is raining or after rain. Land leeches, which are often seen in the mountains, are hermaphroditic and take two months from the time of blood-sucking to the time of egg-laying and hatching. 10 to 50 leeches are born per egg-laying.
Leeches use carbon dioxide and body heat to detect the approach of blood-sucking targets. Their targets are mainly Japanese deers, wild boars, and wild goats, and they also suck the blood of humans.
This site is participating in the 23nd Japan Junior high school/high school Web contest(第23回全国中学高校Webコンテスト).
