


You have to memorize a meteorological symbol, in order to read a weather chart. Japanese style and an international type are shown in a present weather figure, and a meteorological symbol also has two kinds in connection with it. However, expressional width is wide and an international type also has a meteorological symbol in large quantities. Therefore, it is OK if you remember only 21 Japanese-style pieces to draw or read the weather chart in Japan.
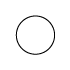
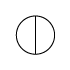
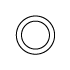
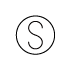
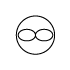
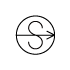
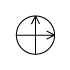
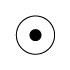
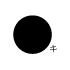
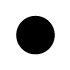
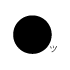
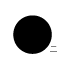
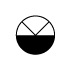
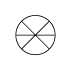
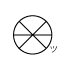
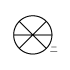
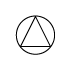
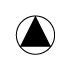
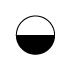
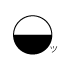
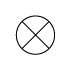

When writing atmospheric pressure, wind force and a wind become important information. The line is pulled by the direction which a wind wipes and a wind looks at wind force by the number of feather. Incidentally, when wind force is 0, it does not write. When actually writing a wind, a top is generally north (direction of ruled line) written in the 16 directions.
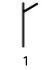
Smoke flutters and it turns out that there is a wind.
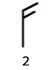
A wind is felt for a face and leaves move.
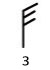
A light flag opens and a thin sprig moves continuously.

Dust leaves and paper soars.

A low tree with a leaf begins to shake and a wave is located on a pond.

A limb moves and an electric wire sounds. It is hard to put an umbrella.
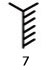
The Kimata object shakes and it is hard to walk toward a wind.

He cannot walk, if a sprig breaks and it goes to a wind.

A tile flies or a chimney falls.

A tree falls completely and damage of a house is serious.

Damage arises in the wide range.

Major injury arises.

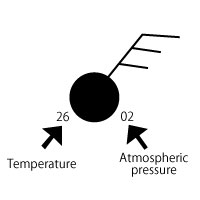
The above-mentioned sign is combined and what wrote atmospheric pressure to the right and wrote temperature to the left becomes a meteorological symbol actually written to a weather chart.
In this case, It becomes "In Naha, winds are the wind force 3 and fine, 2 hPa, and 26 ℃,blowing from southeast."




