Protein synthesis ~Development~
In the previous page, we briefly discussed the mechanism of protein synthesis, but let's take it a step further here.
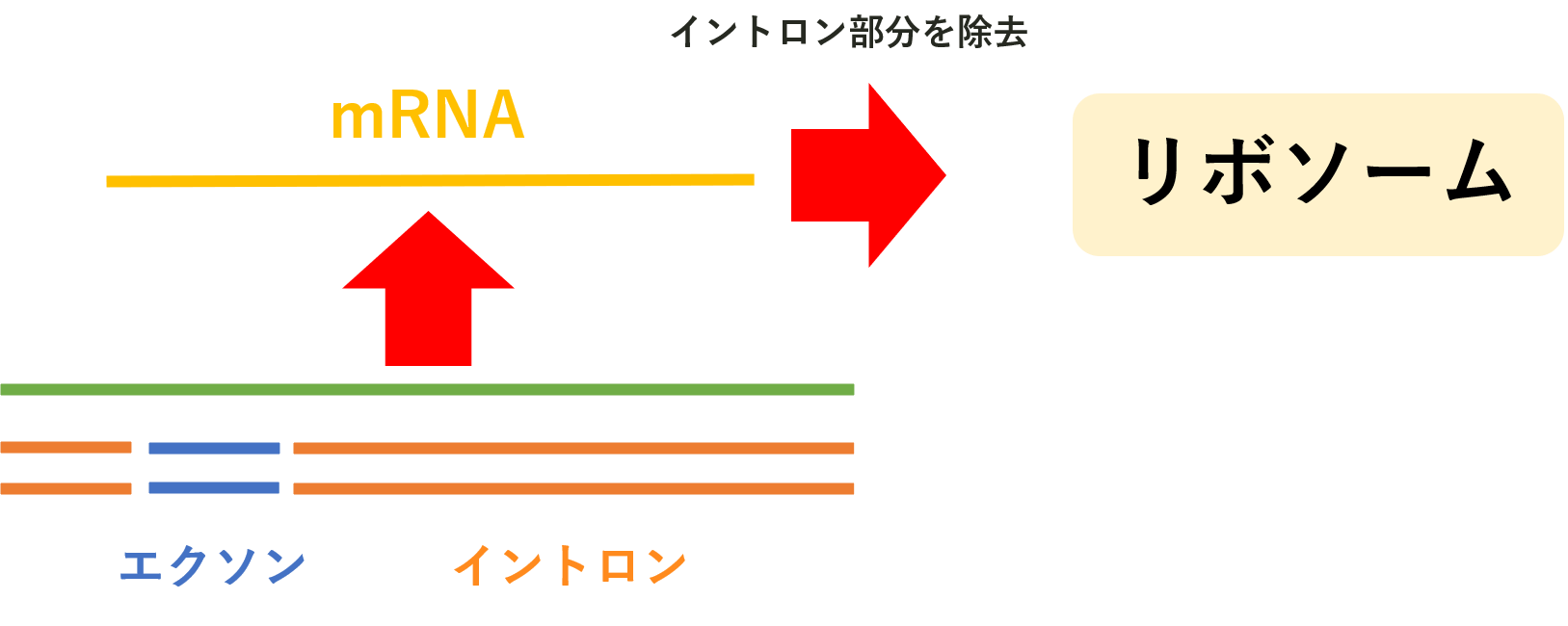
DNA is divided into two parts: the exons, which are used for protein synthesis, and the introns, whose role is still unknown. The exons contain the protein recipe, that is, the information about what amino acids to use. The mRNA that transcribes this information travels to the ribosome for protein synthesis. tRNA is responsible for carrying the amino acids. In addition, tRNAs have a role in recognizing mRNAs that deliver amino acids. See the figure below.
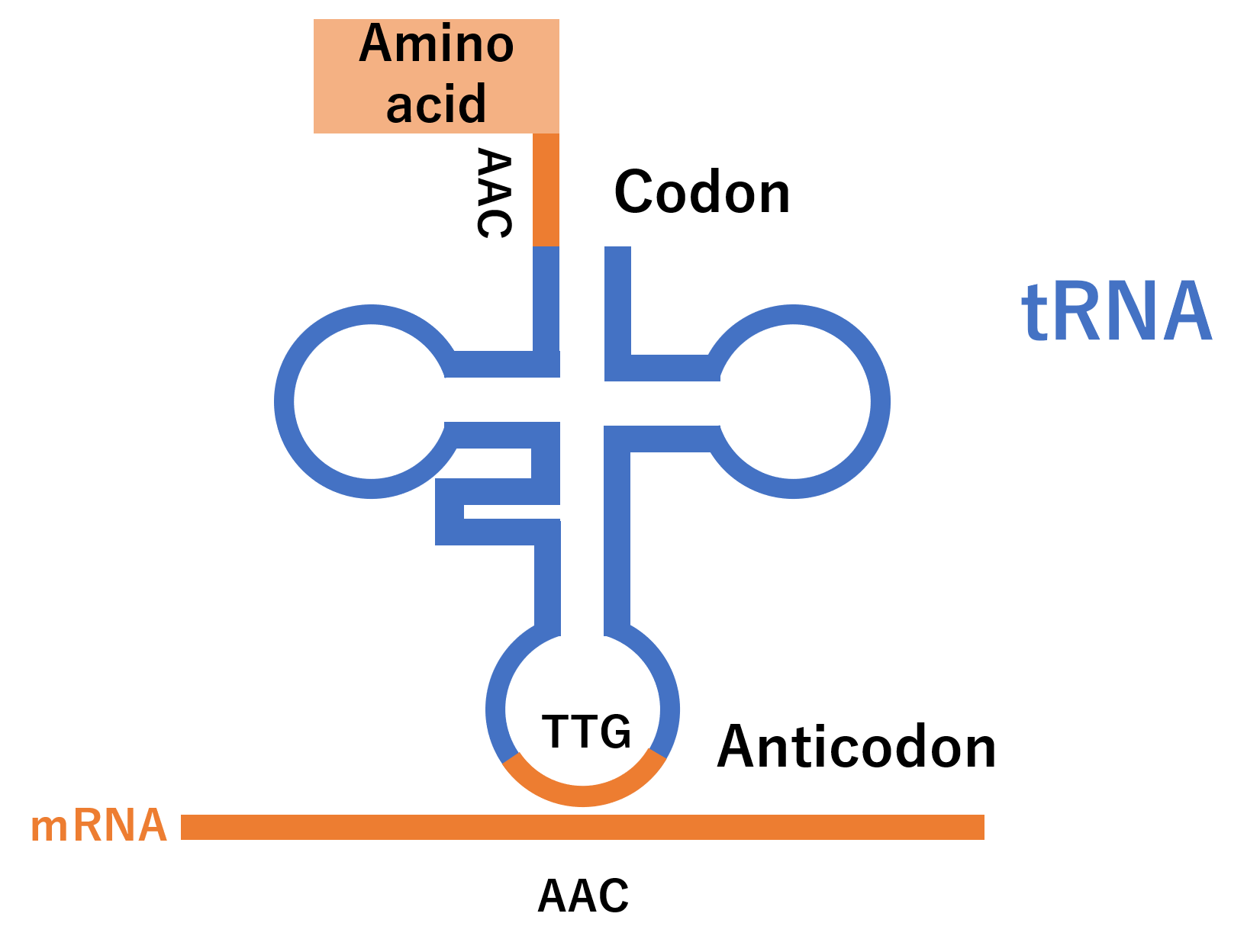
The tRNA has a folded structure, and there are two places where there are no base pairs. The top one is called "codon" and the bottom one is called "anticodon". Codons are attached to amino acids, and anticodons have complementary bases to mRNA, so they form base pairs. tRNA delivers amino acids to mRNA in this way.
Finally, there is rRNA, whose main role is protein synthesis as described on the previous page. rRNA also plays a role in determining whether tRNA and mRNA are in the right combination.

