DNA replication
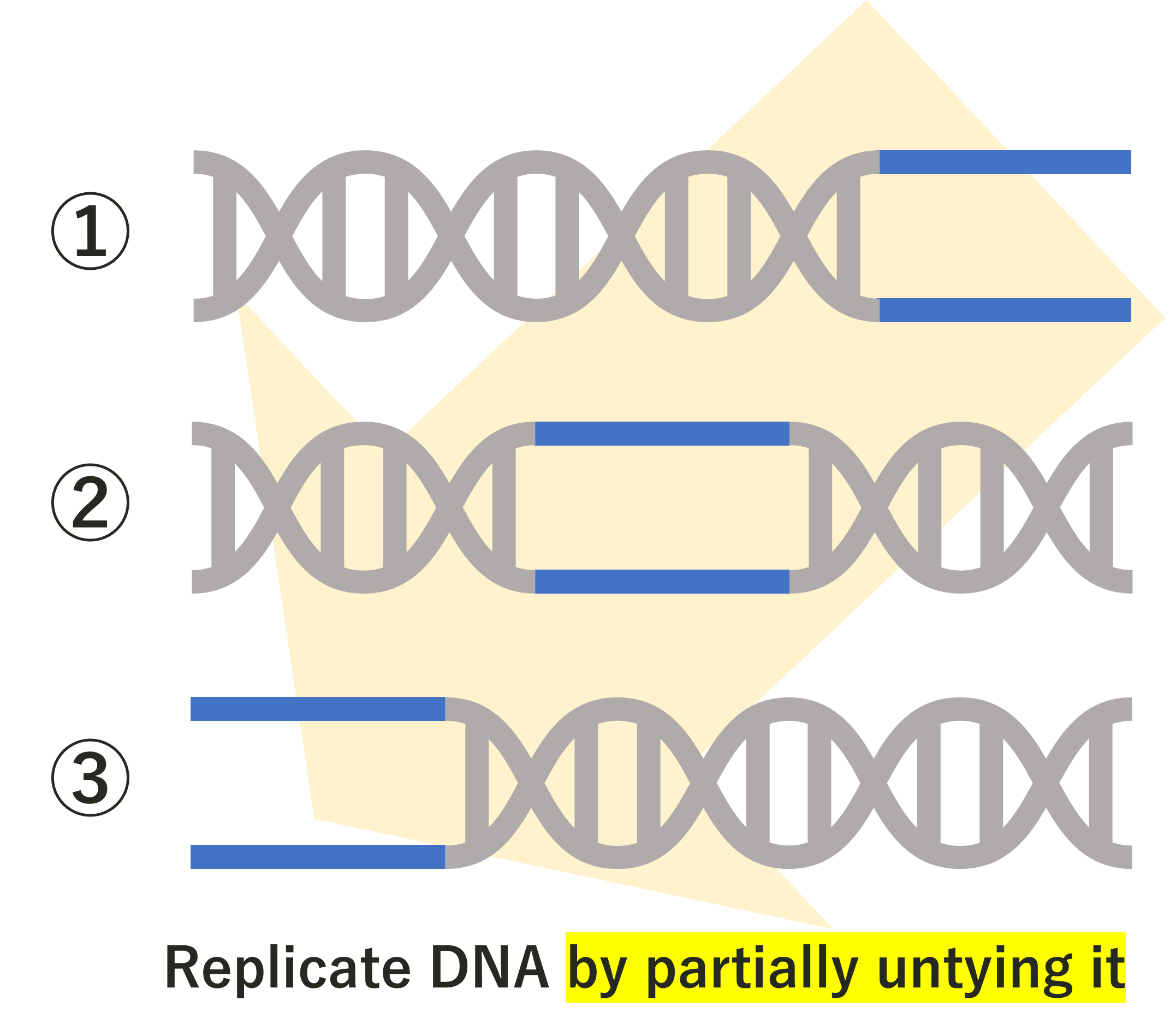
When a chromosome divides, its DNA must also replicate at the same time. So how is DNA replicated? When DNA replicates, it does so in what is called "semi-conservative replication". In semi-conservative replication,
the DNA is not completely broken down, but is replicated by "untying" parts of it, as shown in the figure below.
This is the reason why it is called "semi-conservative".
Protein synthesis
The main role of DNA is to make proteins, which is why DNA is sometimes referred to
as the blueprint of life. So how do we make proteins?
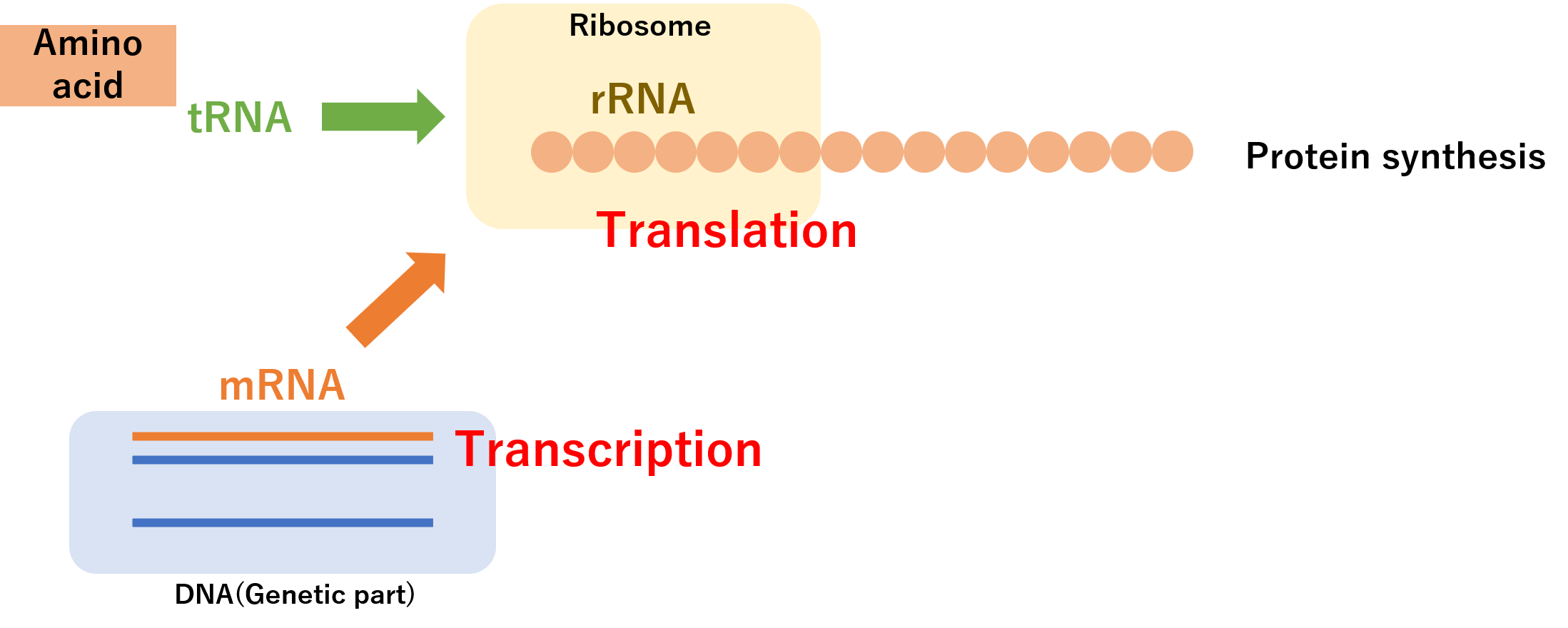
Three types of RNA, "mRNA", "tRNA", and "rRNA", play an active role in protein synthesis. As shown in the figure above, mRNA obtains the protein recipe from DNA and transcribes it.
The tRNA carries the amino acids necessary for protein synthesis, and the rRNA synthesizes the protein in the ribosome. This is how proteins are synthesized.