Learn more about the structure of antibodies
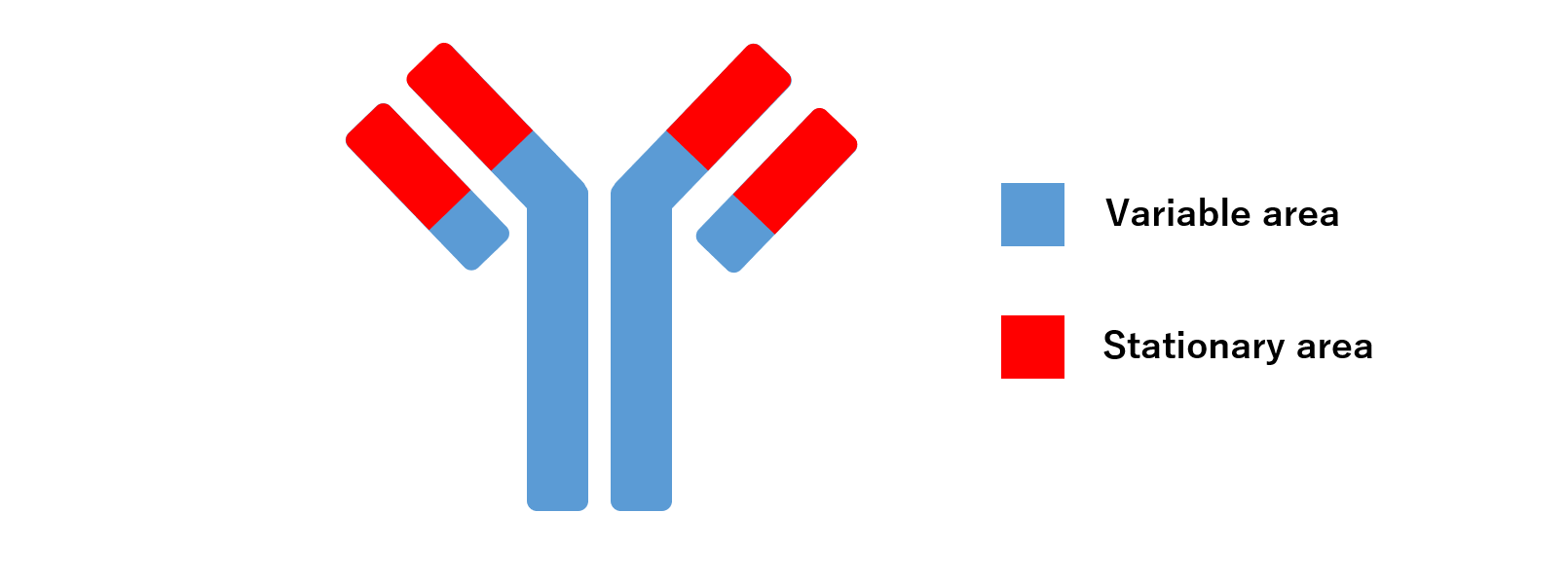
Antibodies can be divided into variable and stationary regions.
As the name suggests, the variable region can change its shape and bind to foreign substances.
The structure of the variable region varies from antibody to antibody, so it can bind to a variety of foreign substances.
This is the structure of the antibody that does not change.
Degradation by pepsin
When the antibody is exposed to the enzyme papain,
it can be broken down into three parts because the disulfide bonds that bind
the antibody are broken down and the antibody is cleaved. Of these,
the two on the variable region side are called the Fab region and the other is called
the Fc region. The Fab region binds with disulfide bonds to form the variable region, while the Fc region plays a role in promoting the release of substances that regulate the function of macrophagy, etc.
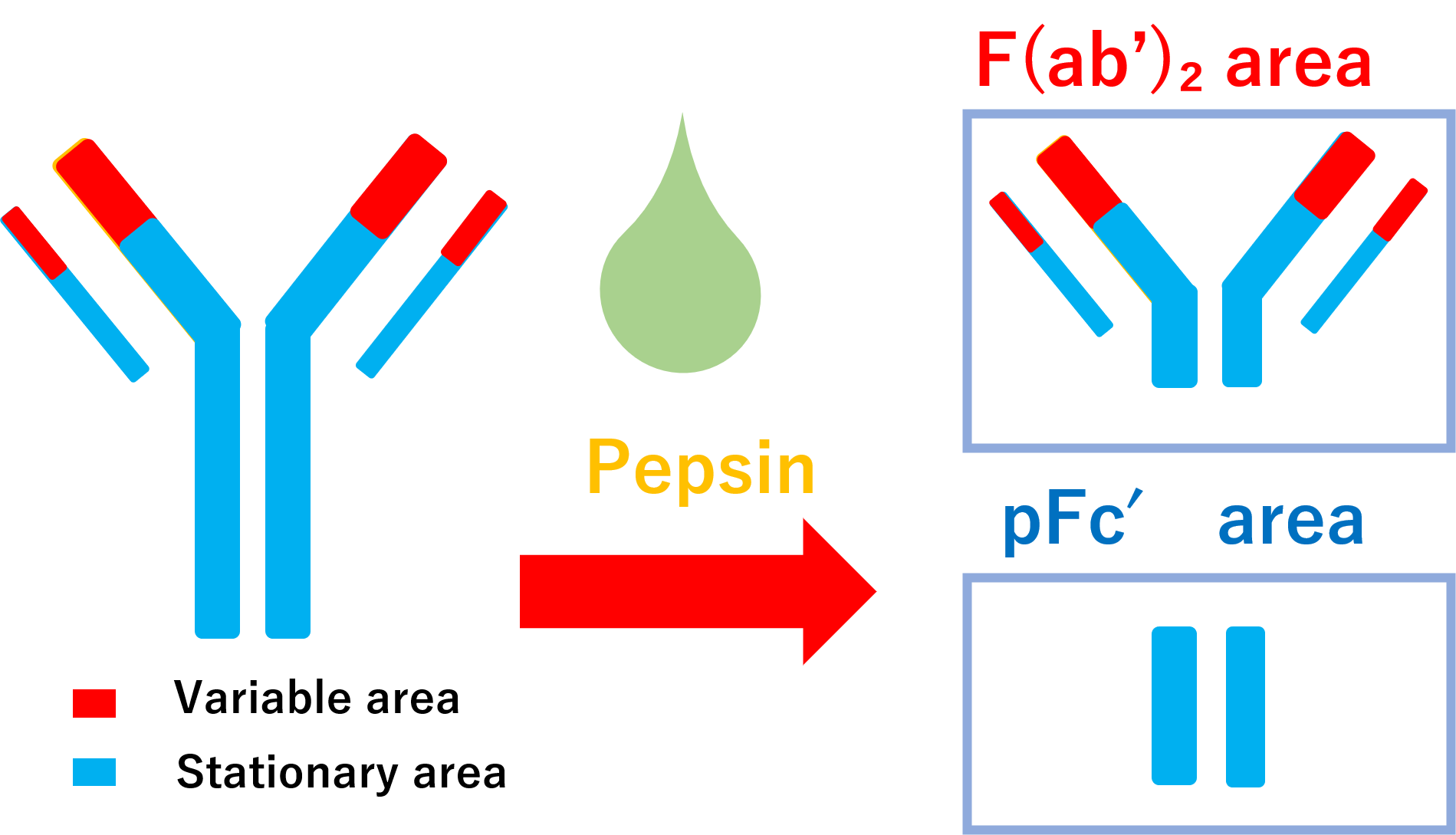
Degradation by pepsin
When antibodies are exposed to pepsin, which is secreted in the stomach, they are degraded in a different way than papain. Pepsin degradation leaves the disulfide bonds intact, unlike papain degradation.