How do biopharmaceuticals work?
How do biopharmaceuticals work in the body? There are biopharmaceuticals that replenish the proteins produced in the body and those that suppress the movement of foreign substances that cause disease. Let's start by looking at biopharmaceuticals that supplement proteins.
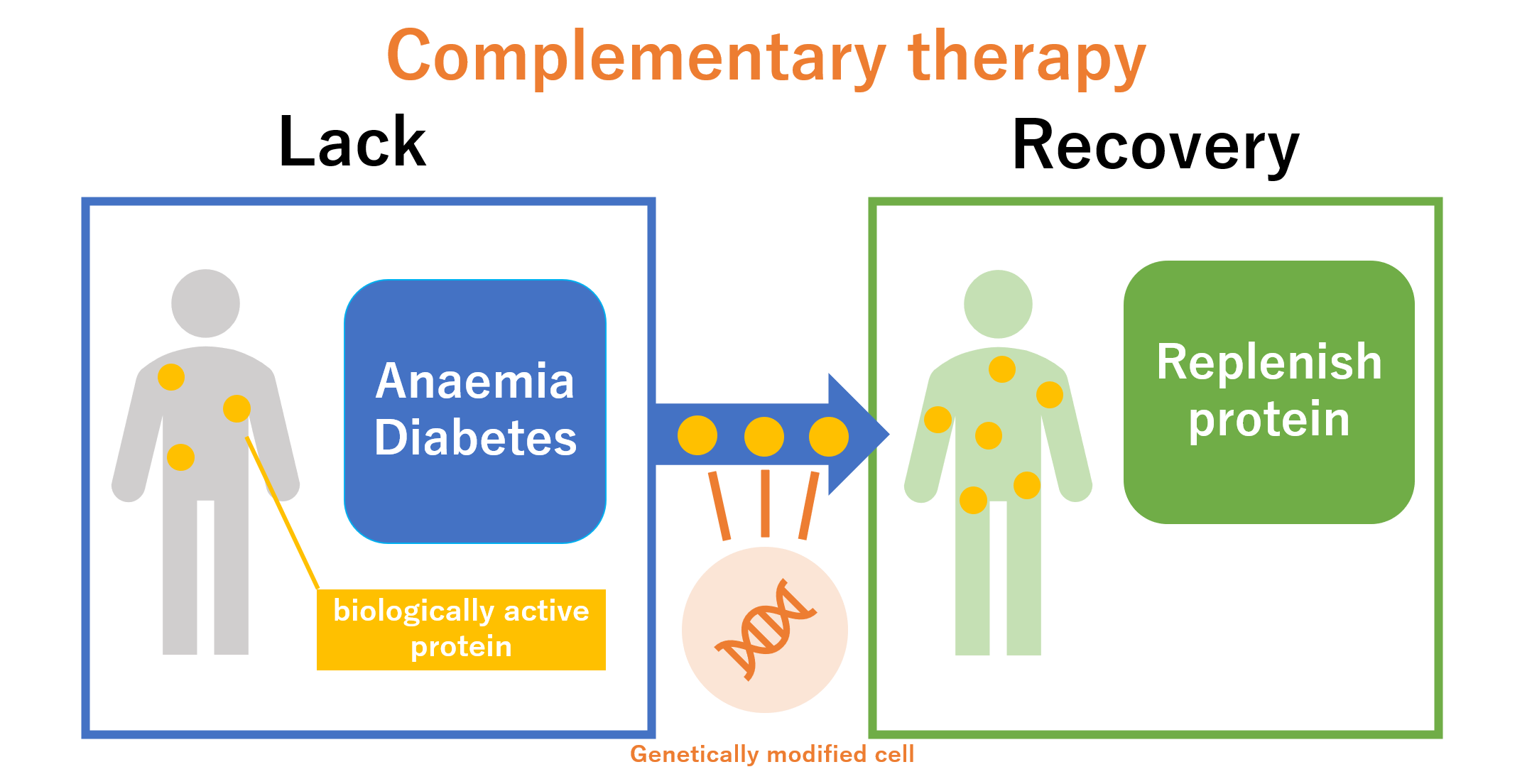
Supplementing missing proteins
In the human body, various proteins work to keep us healthy. These proteins are specifically called bioactive proteins, and their deficiency can lead to diseases such as diabetes and anemia. Therefore, in order to replenish proteins, biotechnology such as genetic recombination was used to artificially create proteins and turn them into drugs, which is the beginning of biopharmaceuticals. This therapy is called "replacement therapy". So far, few small-molecule drugs that work to supplement proteins have been published, and biopharmaceuticals are considered to be important.