Antibody drugs
In the spotlight! Monoclonal antibodies
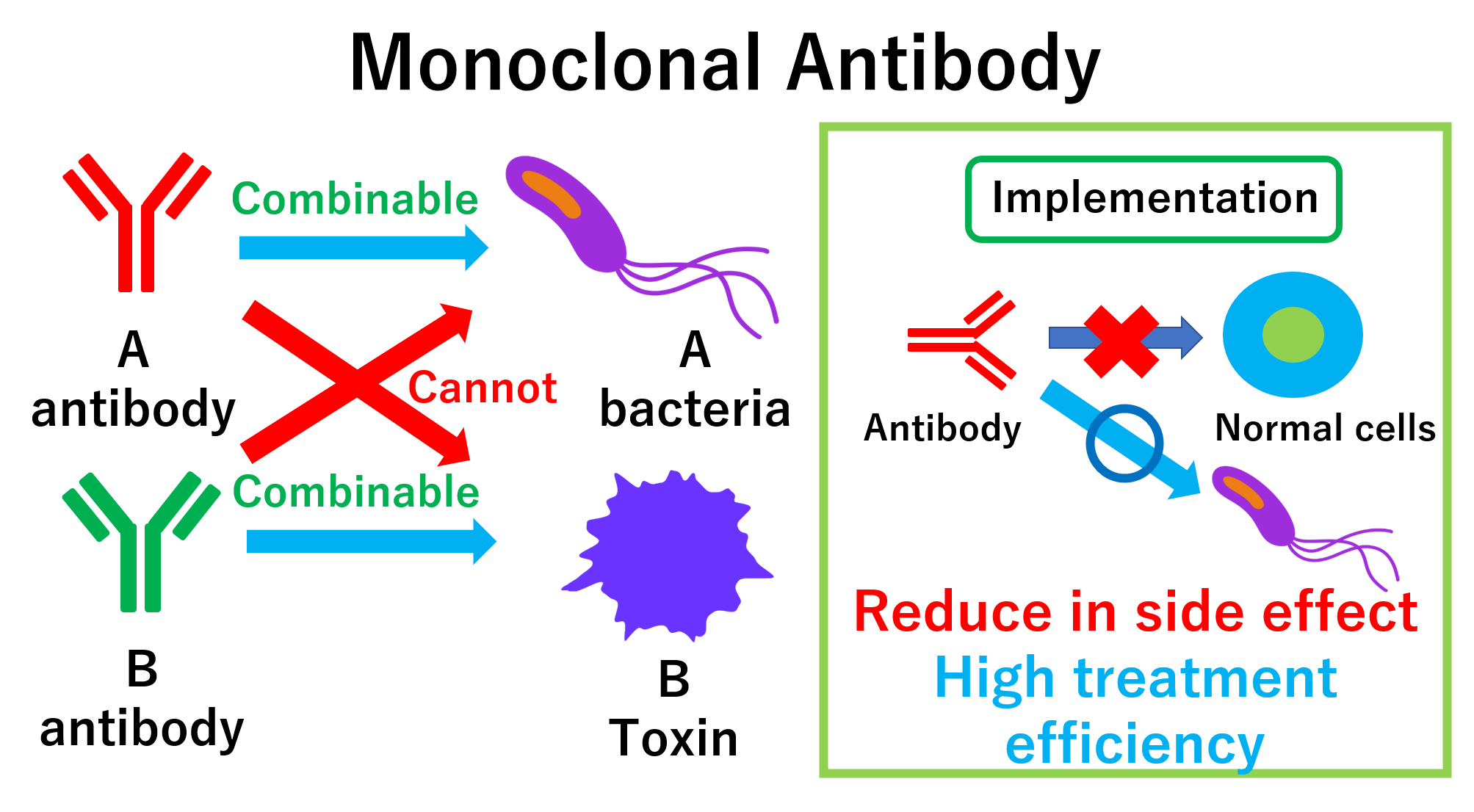
Monoclonal antibodies are the most commonly used antibody drugs today. As the name implies, monoclonal antibodies are produced from a single B cell (mono) and do not contain any genes (clonal),
so they can only bind to one type of antigen. By taking advantage of this ability to act only on specific antigens, it is possible to develop drugs with fewer side effects and higher therapeutic efficiency.
Types of monoclonal antibodies
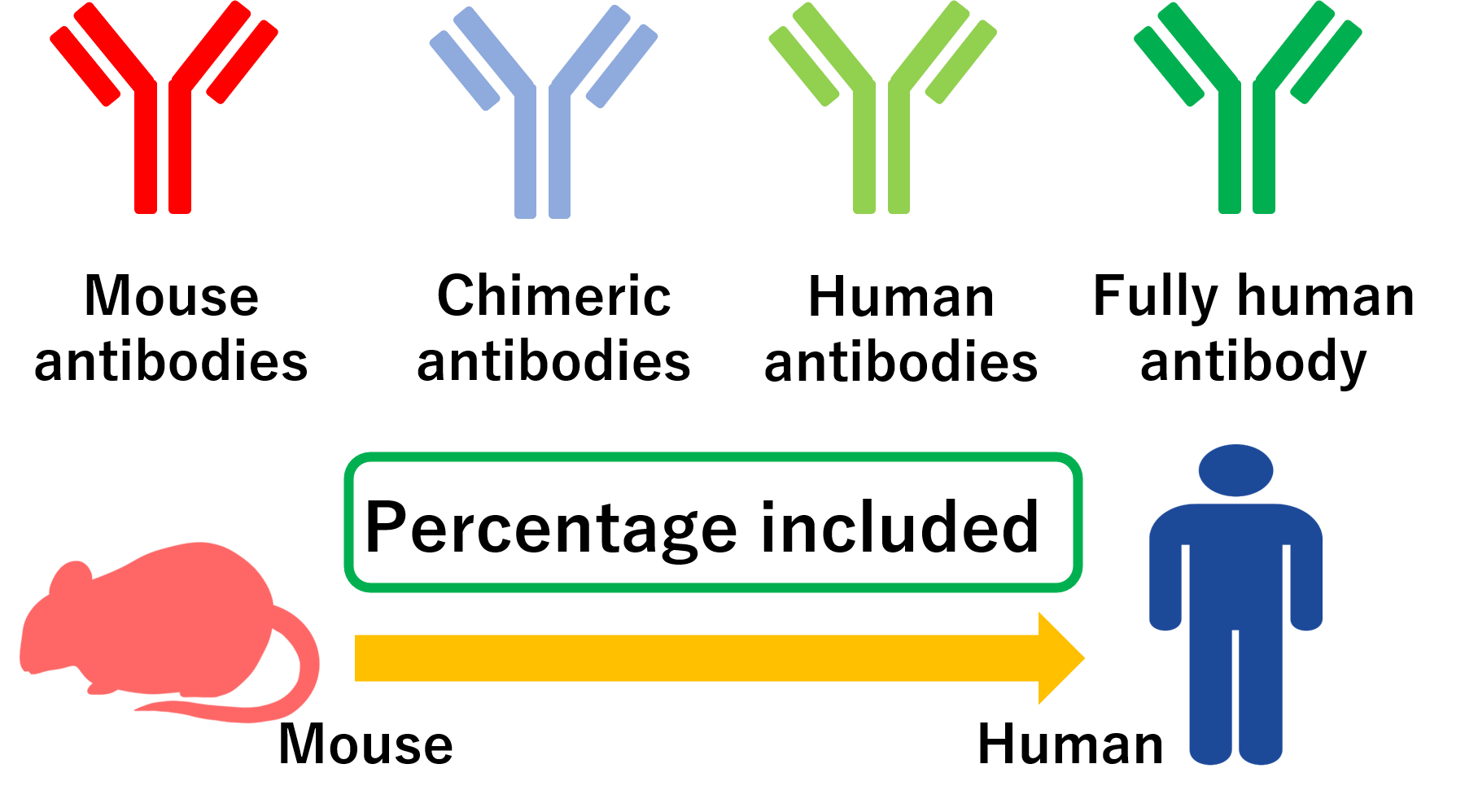
Monoclonal antibodies in the medical field can be divided into four types: mouse antibodies,
chimeric antibodies, humanized antibodies, and fully human antibodies.
The difference between these four types lies in the percentage of human antibodies used.
Conventional drugs that use mouse antibodies are easy to manufacture, but there is a risk that our immune system will recognize them as foreign and cause an allergic reaction.
This is why chimeric antibodies, in which only the variable region of the antibody is left from the mouse, and humanized antibodies have been developed to increase safety. Recently,
research into fully human antibodies that do not use mouse antibodies is also underway.