Domain names and host names are strings of characters that are given for easy human recognition, but actual communication uses IP addresses.
In other words, the domain name or host name must be converted to an IP address. This is called name resolution, and the mechanism that provides this service is called DNS.
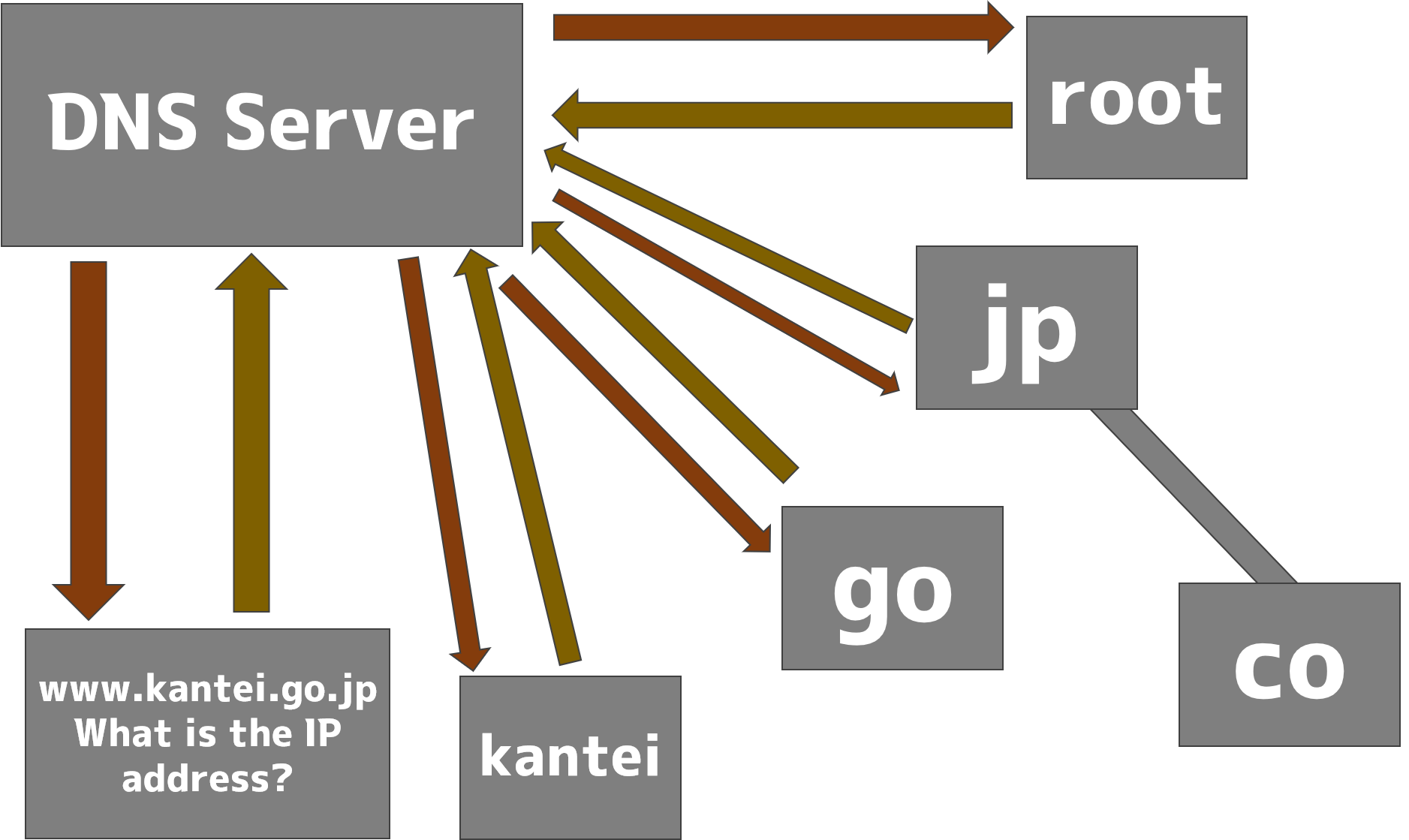
DNS servers can store IP addresses for sites that are used by many people, such as YouTube and Twitter. However, for sites that are used by only a few people, the DNS server does not remember them, so it tries to resolve the name to the root name server. Then, we repeat the process of asking the DNS server that manages jp to tell us its IP address.
Finally, when the IP address is known, ask the DNS server to tell you the IP address and try to connect. This process of converting a domain name to an IP address is called a "positive lookup" and is characterized by the fact that it takes an extremely short time.

Top > Network > Introduction of network > DNS
DNS