Applications in Logistics
About Cold Chain
A cold chain is a type of logistics system that keeps perishable foods and medicines at low temperatures during the production, transportation, and consumption processes.
With the advent of the cold chain, logistics has advanced dramatically. The cold chain has made it possible to deliver a wide variety of products with high freshness and quality. It can be used for a variety of products such as pharmaceuticals, chemicals, blood packs, fresh foods, and frozen foods.
The cold chain plays a very important role not only in the food sector but also in the medical sector.
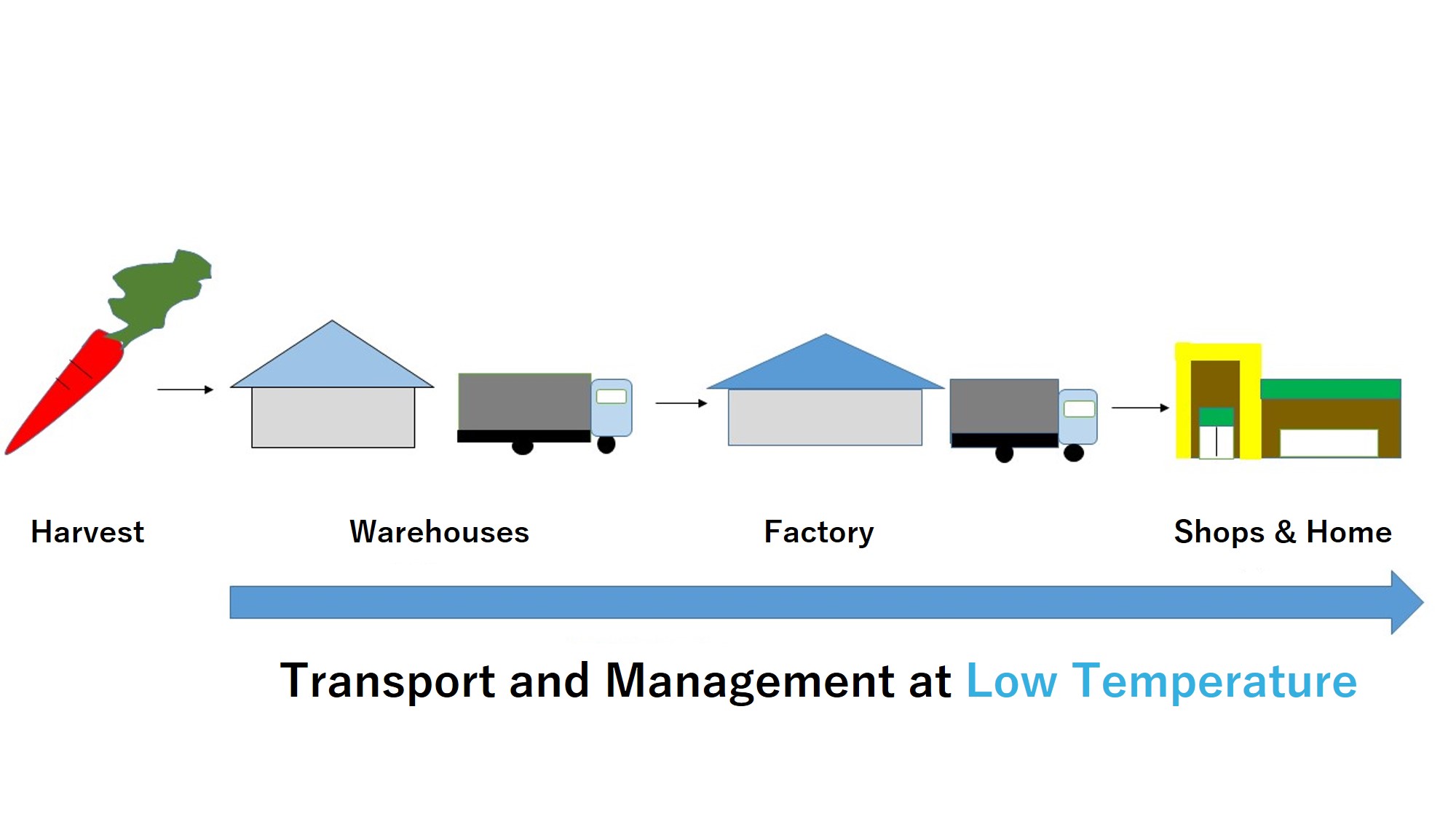
System of Cold Chain
The flow, products from procurement of raw materials, production, inventory management, delivery, sales, and consumption, is called “supply chain.” The cold chain is the process that keeps this supply chain in low temperature. In the past, when we only had normal transportation, we could only transport in very limited areas. Thanks to the cold chains, now, we can buy ice creams and frozen foods at our local convenience store and supermarket.
Advantages of Cold Chain
Reduce Food Loss
Some food products can extend their shelf life and consumption date if they are stored at low temperatures. If these products are stored at room temperature, the quality of the products will deteriorate faster and the sell-by date will be much shorter. Products that are not sold out by the expiration date are discarded, resulting in increased food loss. Cold chain extends the sales period of products and reduces food loss.
Any Products Can be Delivered to AnyWhere
A company that does not have a store in every region of the country can sell its products across the country via cold chain. It costs a lot of money to have stores in multiple regions. Thanks to the cold chains, people don’t need their own stores ,and also, even products that require temperature control can be delivered nationwide.
Possible to Transport Medical Products that Require Low-Temperature Delivery
Medical products, such as vaccines and blood for transfusion, must be delivered at low temperatures, which was problematic before the advent of the cold chain. The controlled temperature range was 2℃ (35.6℉) to 8℃ (46.4℉), and blood for transfusion had to be destroyed if the temperature reached above and below 1℃ (33.8℉). With the cold chains, medical supplies can now be delivered to hospitals and pharmacies without waste. Now, the cold chain is an important part of the medical field. Medical products, which need delicate management, have to guarantee temperature control and quality assurance. “Data loggers” and “temperature control seals” are used to prove that the product was maintained at the required temperature during the transportation.
The old chain has made it possible to reduce food losses and to transport products that require temperature control. It has also made it possible to transport blood transfusions and vaccines, which are difficult to control the temperature, to medical facilities.