Quick Freeze
Propose and Benefits of Development
Have you ever heard the word “quick freezing”? Quick freezing was developed to reduce the quality deterioration that is a drawback of the slow freezing air blast method. By shortening the time taken to pass through the maximum ice crystal formation temperature zone, quick freezing prevents the ice crystals from growing larger and protects the quality.
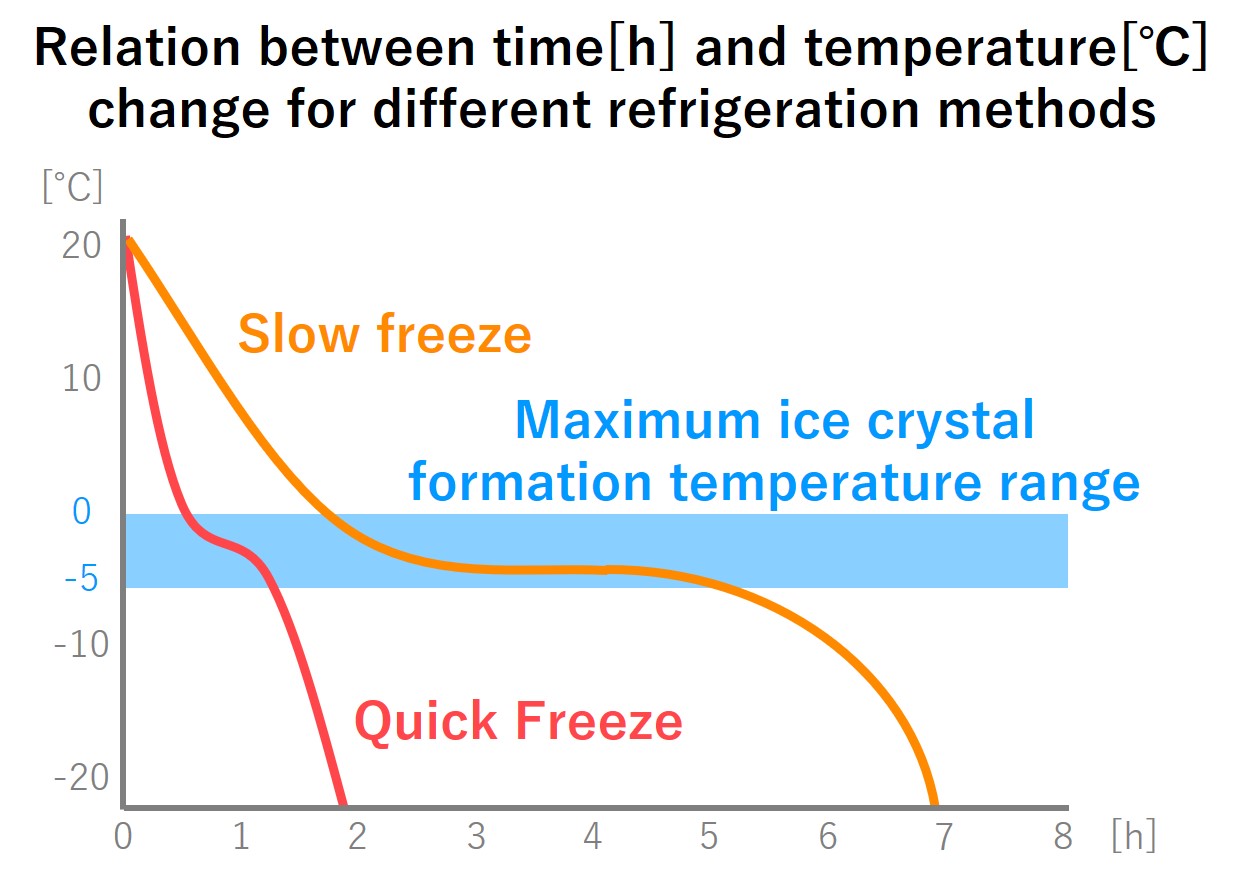
Quick freezing contributes to the reduction of storage and distribution costs because the time spent on freezing has been reduced. Furthermore, it is not affected by the season of materials or price fluctuations of products, thus enabling the long-term preservation of food products.
Various Refrigeration Systems
Quick freezing is achieved by either fast reducing the temperature of the medium or rapidly releasing the heat of the food. The three types of freezing procedures listed below are examples.
Brine System (Liquid Method)
Freezing is done by putting food in a liquid that has been cooled to -10℃ (14℉) to -35℃ (-31℉). The medium is liquids that do not coagulate even at 0℃ (32℉), such as alcohol.
Contact Method
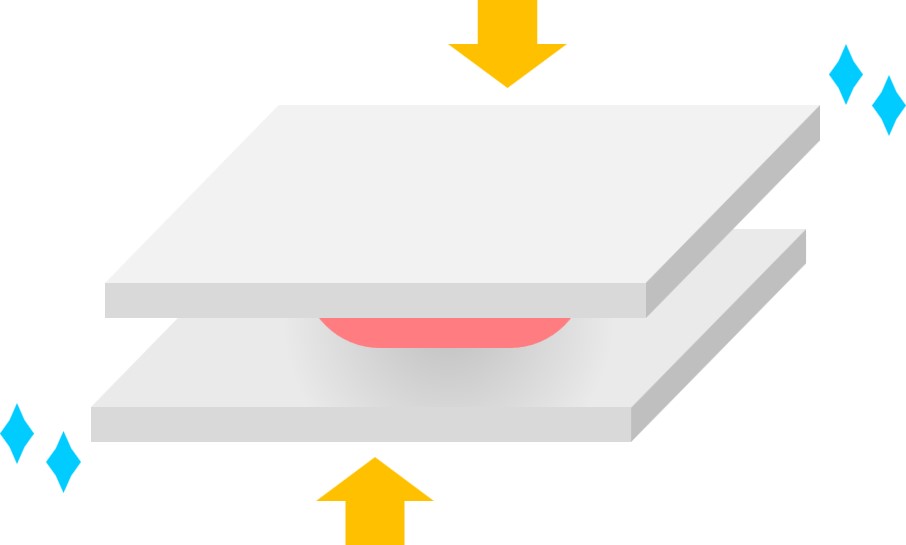
Food is frozen by contacting it with a low-temperature freezer plate. This freezing process is based on the fact that the quantity of heat transferred through the freezer plate is larger than that of air. There are further gadgets that increase cooling technology by putting pressure on the freezer plate.
Liquid Gas Method
Catalysts with extremely low temperatures, such as liquid nitrogen (approx. -196℃, -320.8℉) and liquefied carbon dioxide (approx. -79℃, -110.2℉), are sprayed directly over the food to freeze it.
Furthermore, the air-blast method has been utilized as a quick-freezing technology by lowering the temperature of the air delivered into the system.
There are facilities in the refrigeration industry that incorporate numerous processes. Users must choose the most appropriate freezing method based on the product to be frozen.
Quick freezing technology has been developed to solve the problem of slow freezing, which results in deterioration of quality. There are various methods of quick freezing, which can be used to reduce transportation and storage costs.