
Medical
Table of Contents
Immune rejection is caused by the immune system identifying the transplant as foreign, generating a response that will harm the transplanted organ. Accordingly, donors and patients should be carefully matched so as not to risk the patients. The additional option is to administer immunosuppressive drugs to suppress rejection.
Some patients cannot have organ transplants due to a lack of donors. The number of patients who need organs outnumbers that of donors who agree to donate organ.
 Regenerative medicine is a method of regenerating organs that have lost their functions by extracting special cells called stem cells from the body, increasing the number of organs, and then transplanting them back into the original body. The recent development of iPS cells is partially included in this process. has been attracting attention since the 1980s to have the potential to address the issues of immune rejection and a lack of donors.
Regenerative medicine is a method of regenerating organs that have lost their functions by extracting special cells called stem cells from the body, increasing the number of organs, and then transplanting them back into the original body. The recent development of iPS cells is partially included in this process. has been attracting attention since the 1980s to have the potential to address the issues of immune rejection and a lack of donors.
 Regenerative medicine is a method of regenerating organs that have lost their functions by extracting special cells called stem cells from the body, increasing the number of organs, and then transplanting them back into the original body. The recent development of iPS cells is partially included in this process. is a technology in which cells collected from patients or tissue donors are cultured in large quantities outside the body to secure sufficient quantities of the necessary cells to build the desired tissue structure, which is then transplanted back into the patient.
Regenerative medicine is a method of regenerating organs that have lost their functions by extracting special cells called stem cells from the body, increasing the number of organs, and then transplanting them back into the original body. The recent development of iPS cells is partially included in this process. is a technology in which cells collected from patients or tissue donors are cultured in large quantities outside the body to secure sufficient quantities of the necessary cells to build the desired tissue structure, which is then transplanted back into the patient.
 Regenerative medicine is a method of regenerating organs that have lost their functions by extracting special cells called stem cells from the body, increasing the number of organs, and then transplanting them back into the original body. The recent development of iPS cells is partially included in this process. to preventing immune rejection.
Regenerative medicine is a method of regenerating organs that have lost their functions by extracting special cells called stem cells from the body, increasing the number of organs, and then transplanting them back into the original body. The recent development of iPS cells is partially included in this process. to preventing immune rejection. Regenerative medicine is a method of regenerating organs that have lost their functions by extracting special cells called stem cells from the body, increasing the number of organs, and then transplanting them back into the original body. The recent development of iPS cells is partially included in this process. is still not accepted as a standard medicine; therefore, it is necessary to create an environment where patients receive the treatment and progress the technology.
Regenerative medicine is a method of regenerating organs that have lost their functions by extracting special cells called stem cells from the body, increasing the number of organs, and then transplanting them back into the original body. The recent development of iPS cells is partially included in this process. is still not accepted as a standard medicine; therefore, it is necessary to create an environment where patients receive the treatment and progress the technology.
 Regenerative medicine is a method of regenerating organs that have lost their functions by extracting special cells called stem cells from the body, increasing the number of organs, and then transplanting them back into the original body. The recent development of iPS cells is partially included in this process., including fabricating cell tissues with bio-3D printers.
Regenerative medicine is a method of regenerating organs that have lost their functions by extracting special cells called stem cells from the body, increasing the number of organs, and then transplanting them back into the original body. The recent development of iPS cells is partially included in this process., including fabricating cell tissues with bio-3D printers.
 Regenerative medicine is a method of regenerating organs that have lost their functions by extracting special cells called stem cells from the body, increasing the number of organs, and then transplanting them back into the original body. The recent development of iPS cells is partially included in this process. invented by Cyfuse works. The most important part of it is that the cells come from patients.
Regenerative medicine is a method of regenerating organs that have lost their functions by extracting special cells called stem cells from the body, increasing the number of organs, and then transplanting them back into the original body. The recent development of iPS cells is partially included in this process. invented by Cyfuse works. The most important part of it is that the cells come from patients.
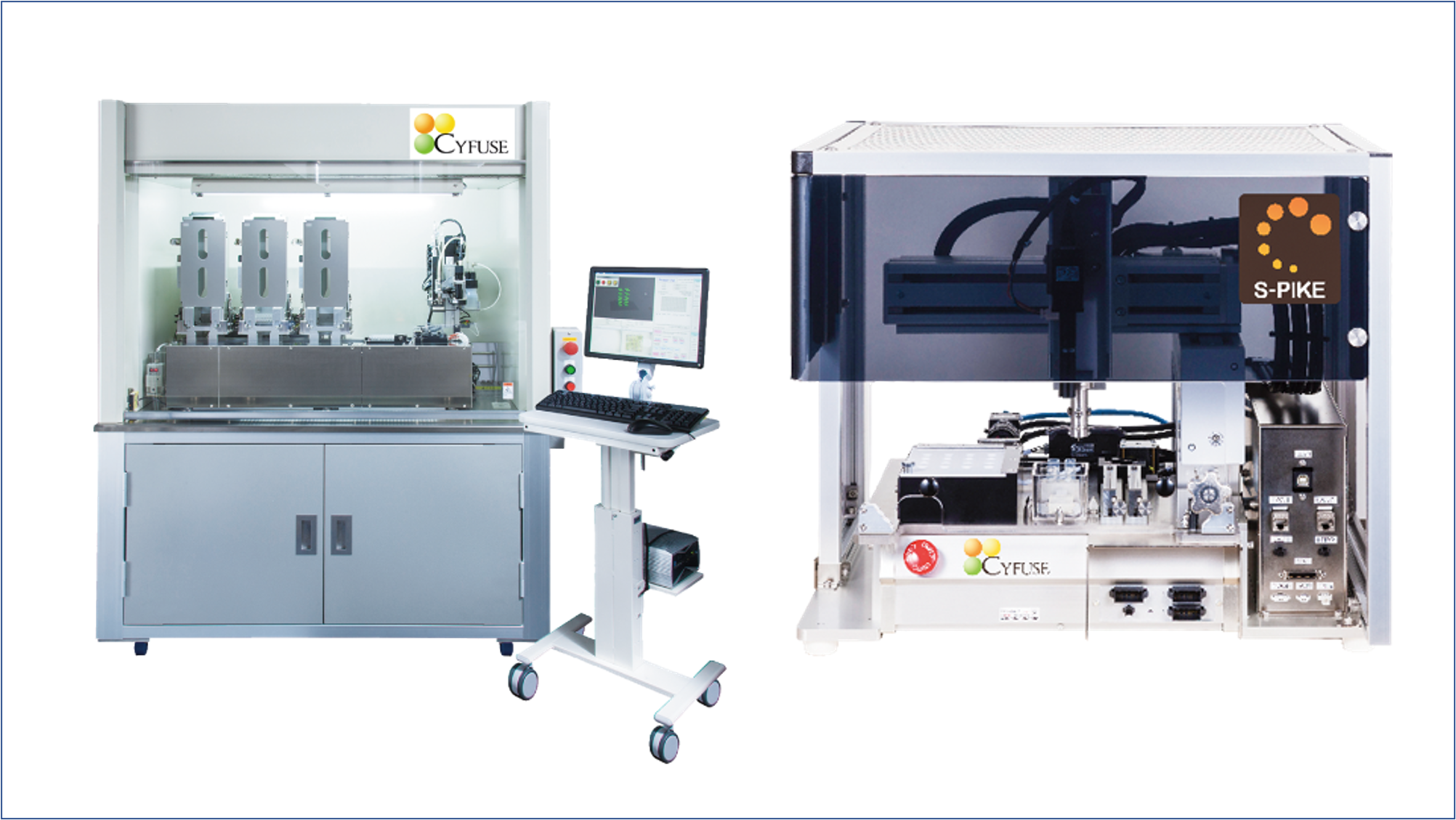

Provided by Cyfuse
▲Bio 3D printer "regenova" (left) and "S-PIKE" (right) developed by Cyfuse.
 Regenerative medicine is a method of regenerating organs that have lost their functions by extracting special cells called stem cells from the body, increasing the number of organs, and then transplanting them back into the original body. The recent development of iPS cells is partially included in this process. and 3D printers on August 22nd, 2022.
Regenerative medicine is a method of regenerating organs that have lost their functions by extracting special cells called stem cells from the body, increasing the number of organs, and then transplanting them back into the original body. The recent development of iPS cells is partially included in this process. and 3D printers on August 22nd, 2022.

Place: Member's home
▲Appearance of Interview
Q.1
What kind of research are you working on?
A.1
We utilize the fields of biology and engineering for our research and apply the areas to regenerative medicine Regenerative medicine is a method of regenerating organs that have lost their functions by extracting special cells called stem cells from the body, increasing the number of organs, and then transplanting them back into the original body. The recent development of iPS cells is partially included in this process. and developing new drugs, providing them for the front lines of health care. In particular, bio-3D printers enable us to create tissues and organs.
Regenerative medicine is a method of regenerating organs that have lost their functions by extracting special cells called stem cells from the body, increasing the number of organs, and then transplanting them back into the original body. The recent development of iPS cells is partially included in this process. and developing new drugs, providing them for the front lines of health care. In particular, bio-3D printers enable us to create tissues and organs.
Q.2
How did you come to work on this project?
A.2
Creating cell products with bio-3D printers is unprecedented in the long history of medical science. Accordingly, this technology will play a significant role in medicine and be one of the patients' choices, leading to better medical care.
Q.3
What are some of the current issues in the medical field that you are trying to solve with 3D printers?
A.3
As mentioned, we are doing this research to contribute to patients by providing them choices for their treatment. Therefore, we are creating some new possibilities, not finding problems.
Q.4
What do you envision as the ideal image of "medicine" x "3D printer"?
A.4
Our ideal image of the project is to create a medical care system where everyone can receive treatment without worry.
Q.5
What is the meaning of the term "regenerative medicine Regenerative medicine is a method of regenerating organs that have lost their functions by extracting special cells called stem cells from the body, increasing the number of organs, and then transplanting them back into the original body. The recent development of iPS cells is partially included in this process."?
Regenerative medicine is a method of regenerating organs that have lost their functions by extracting special cells called stem cells from the body, increasing the number of organs, and then transplanting them back into the original body. The recent development of iPS cells is partially included in this process."?
A.5
We use the term "regenerative medicine Regenerative medicine is a method of regenerating organs that have lost their functions by extracting special cells called stem cells from the body, increasing the number of organs, and then transplanting them back into the original body. The recent development of iPS cells is partially included in this process." to create a new medicine that can cure illnesses and heal injuries that have been considered impossible.
Regenerative medicine is a method of regenerating organs that have lost their functions by extracting special cells called stem cells from the body, increasing the number of organs, and then transplanting them back into the original body. The recent development of iPS cells is partially included in this process." to create a new medicine that can cure illnesses and heal injuries that have been considered impossible.
Preserving human organs is difficult, as they are biodegradable. How do you manage that?
Since organs are made up of cells, it is very important to supply the organs with abundant oxygen and nutrients. Also, germs are a cause of rotting. Accordingly, we preserve organs in a sterile environment and immerse them in culture media that contains oxygen and nutrient. We also stir culture media to supply the organs with enough oxygen and nutriention more effectively.
Q.6
What are some of the problems you are currently facing?
A.6
The problems we are facing are as follows:
The current agendas
1.Spreading the term "regenerative medicine Regenerative medicine is a method of regenerating organs that have lost their functions by extracting special cells called stem cells from the body, increasing the number of organs, and then transplanting them back into the original body. The recent development of iPS cells is partially included in this process."
Regenerative medicine is a method of regenerating organs that have lost their functions by extracting special cells called stem cells from the body, increasing the number of organs, and then transplanting them back into the original body. The recent development of iPS cells is partially included in this process."
2.Establishing a system of providing “regenerative medicine Regenerative medicine is a method of regenerating organs that have lost their functions by extracting special cells called stem cells from the body, increasing the number of organs, and then transplanting them back into the original body. The recent development of iPS cells is partially included in this process.”
Regenerative medicine is a method of regenerating organs that have lost their functions by extracting special cells called stem cells from the body, increasing the number of organs, and then transplanting them back into the original body. The recent development of iPS cells is partially included in this process.”
Realizing the two goals is necessary to provide patients with new types of medicine.
In the case of medical drug, for example, we don't have to worry about preserving medicine at a room temperature, or time is not a concern as medicine is made from chemical substances. On the other hand, our products are made from patients' cells; therefore, we need to care about how to preserve them, including temperature. Also, we discuss with delivery companies how to deliver our cellular products to our customers without any damage to the cell tissues.
Q.7
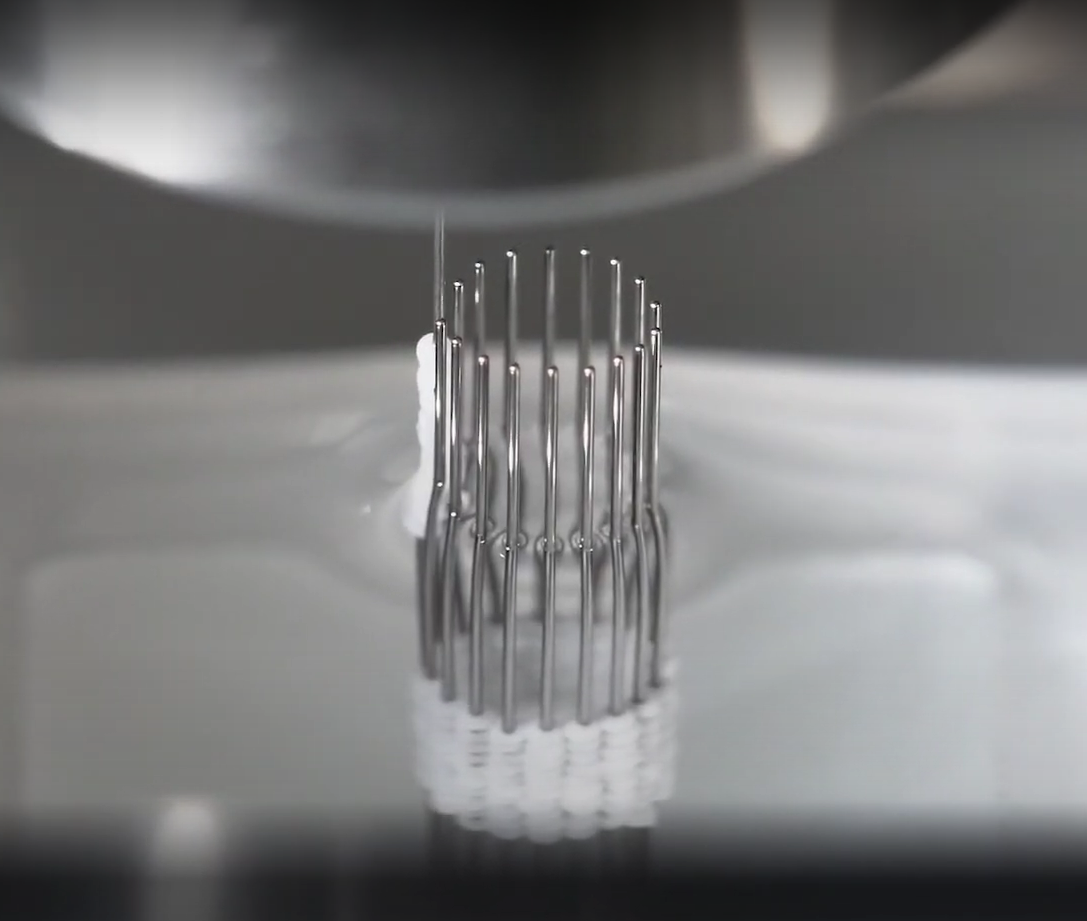
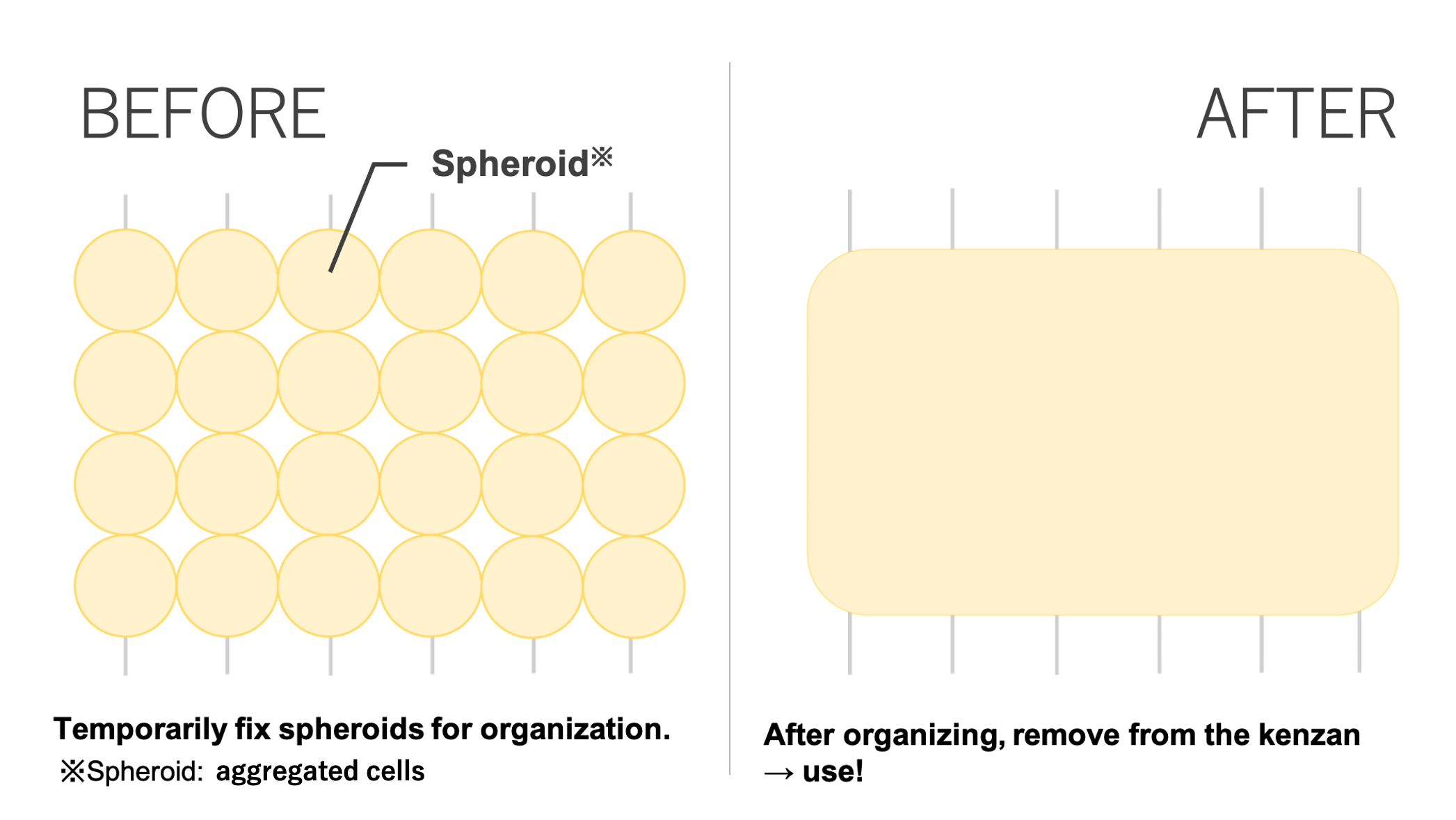
I heard you use a Kenzan for "regenova." How did you come up with the idea of using a Kenzan?
A.7
Prof. Nakayama who is the inventor of our bio-3D printer system and a medical doctor of the orthopedic said that he got the idea from the process of fracture treatment that broken bones has been fixed by the metal needle transiently. He imagine, "If I make the cell aggregates and temporarily stuck them on the needle(kenzan), wouldn't it fuse each other as one tissue and then pull it out?" This was the hypothesis that led to the present format.
We are concerned about the cost. Do patients have to pay a lot of money for their treatment? Let us know about the current issue.
We cannot avoid this issue, as culturing and 3D stacking costs a lot, resulting in a high cost of treatment. However, we think that the situation in which the treatment is only available to patients who can afford to receive it is not good in terms of equality. Therefore, we aim to develop new technology for everyone to receive treatment. The first solution is to create a production process that can be realized at a low cost. The other solution is to make the treatment covered by insurance.
The insurance system in Japan is effective to relieve the burden of expenses for patient, so it is important for us to develop a new treatment that are covered by insurance.
Q.8
What makes you stick to using the term "cell-derived"?
A.8
General 3D bioprinters use cells as an ink that has the role of adhesive and creates tissues. Unfortunately, this means we have to use materials that do not exist in our bodies, so there is a risk for safety. Accordingly, we use patients' cells only to create tissues or organs for them.
Q.9
We are creating a website titled "Printer of the Future." What is the "printer of the future" like for you?
A.9
I think "future printers" are 3D printers that will be used in the future to solve all kinds of medical, dermatological, orthopedic, ophthalmological, etc. problems with 3D printers.
This question might be personal, but what made you join Cyfuse?
Before joining Cyfuse, I'd worked for a company that produces plastics. I realized that the company could not be involved with the new treatments for some illnesses. That is why, I decided to join my current workplace to work on a new treatment.
Before joining Cyfuse, I used to work for a game-related entertainment company. I contributed to society by providing games to people of all ages and genders. Then, I started wondering if I would suffer from a severe illness in the future, and I wanted to try a field, so I began to work for my current workplace.